Novel protein-truncating variants of a chromatin-modifying gene MSL2 in syndromic neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 38702431
- PMCID: PMC11219747
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-024-01576-0
Novel protein-truncating variants of a chromatin-modifying gene MSL2 in syndromic neurodevelopmental disorders
Abstract
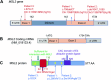
Numerous large scale genomic studies have uncovered rare but recurrent pathogenetic variants in a significant number of genes encoding epigenetic machinery in cases with neurodevelopmental disorders (NDD) especially autism spectrum disorder (ASD). These findings provide strong support for the functional importance of epigenetic regulators in neurodevelopment. After the clinical genomics evaluation of the patients using exome sequencing, we have identified, three novel protein-truncating variants (PTVs) in the MSL2 gene (OMIM: 614802) which encodes a chromatin modifying enzyme. MSL2 modifies chromatin through both mono-ubiquitination of histone 2B on lysine 34 (K34) and acetylation of histone H4 on lysine 16 (K16). We reported first time the detailed clinical features associated with 3 MSL2 PTVs. There are 15 PTVs (13 de novo) reported from the large genomics studies (12 cases) or ClinVar (3 cases) of NDD, ASD, and developmental disorders (DD) but the specific clinical features for these cases are not described. Taken together, our descriptions of dysmorphic face and other features support the causal role of MSL2 in a likely syndromic neurodevelopmental disorder and add MSL2 to a growing list of epigenetic genes implicated in ASD.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Jill A. Rosenfeld is associate with The Department of Molecular & Human Genetics at Baylor College of Medicine which receives revenue from clinical genetic testing completed at Baylor Genetics Laboratories.
Figures

References
-
- Duffney LJ, Valdez P, Tremblay MW, Cao X, Montgomery S, McConkie-Rosell A, et al. Epigenetics and autism spectrum disorder: a report of an autism case with mutation in H1 linker histone HIST1H1E and literature review. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2018;177:426–33. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32631. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

