Tribulations and future opportunities for artificial intelligence in precision medicine
- PMID: 38702711
- PMCID: PMC11069149
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05067-0
Tribulations and future opportunities for artificial intelligence in precision medicine
Abstract
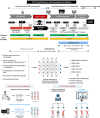
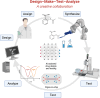
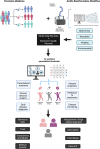
Upon a diagnosis, the clinical team faces two main questions: what treatment, and at what dose? Clinical trials' results provide the basis for guidance and support for official protocols that clinicians use to base their decisions. However, individuals do not consistently demonstrate the reported response from relevant clinical trials. The decision complexity increases with combination treatments where drugs administered together can interact with each other, which is often the case. Additionally, the individual's response to the treatment varies with the changes in their condition. In practice, the drug and the dose selection depend significantly on the medical protocol and the medical team's experience. As such, the results are inherently varied and often suboptimal. Big data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) approaches have emerged as excellent decision-making tools, but multiple challenges limit their application. AI is a rapidly evolving and dynamic field with the potential to revolutionize various aspects of human life. AI has become increasingly crucial in drug discovery and development. AI enhances decision-making across different disciplines, such as medicinal chemistry, molecular and cell biology, pharmacology, pathology, and clinical practice. In addition to these, AI contributes to patient population selection and stratification. The need for AI in healthcare is evident as it aids in enhancing data accuracy and ensuring the quality care necessary for effective patient treatment. AI is pivotal in improving success rates in clinical practice. The increasing significance of AI in drug discovery, development, and clinical trials is underscored by many scientific publications. Despite the numerous advantages of AI, such as enhancing and advancing Precision Medicine (PM) and remote patient monitoring, unlocking its full potential in healthcare requires addressing fundamental concerns. These concerns include data quality, the lack of well-annotated large datasets, data privacy and safety issues, biases in AI algorithms, legal and ethical challenges, and obstacles related to cost and implementation. Nevertheless, integrating AI in clinical medicine will improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes, contribute to more efficient healthcare delivery, reduce costs, and facilitate better patient experiences, making healthcare more sustainable. This article reviews AI applications in drug development and clinical practice, making healthcare more sustainable, and highlights concerns and limitations in applying AI.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Disease diagnosis; Drug discovery and development; Health technology assessment; Machine learning; Precision medicine; Prediction; Prevention.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

