Characterization and classification of ductal carcinoma tissue using four channel based stokes-mueller polarimetry and machine learning
- PMID: 38703302
- PMCID: PMC11069477
- DOI: 10.1007/s10103-024-04056-5
Characterization and classification of ductal carcinoma tissue using four channel based stokes-mueller polarimetry and machine learning
Abstract
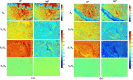
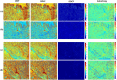
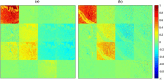
Interaction of polarized light with healthy and abnormal regions of tissue reveals structural information associated with its pathological condition. Even a slight variation in structural alignment can induce a change in polarization property, which can play a crucial role in the early detection of abnormal tissue morphology. We propose a transmission-based Stokes-Mueller microscope for quantitative analysis of the microstructural properties of the tissue specimen. The Stokes-Mueller based polarization microscopy provides significant structural information of tissue through various polarization parameters such as degree of polarization (DOP), degree of linear polarization (DOLP), and degree of circular polarization (DOCP), anisotropy (r) and Mueller decomposition parameters such as diattenuation, retardance and depolarization. Further, by applying a suitable image processing technique such as Machine learning (ML) output images were analysed effectively. The support vector machine image classification model achieved 95.78% validation accuracy and 94.81% testing accuracy with polarization parameter dataset. The study's findings demonstrate the potential of Stokes-Mueller polarimetry in tissue characterization and diagnosis, providing a valuable tool for biomedical applications.
Keywords: Machine learning; Mueller matrix; Polar decomposition; Polarization; Stokes vector; Tissue.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ghosh N, Vitkin AI (2011) Tissue polarimetry: concepts, challenges, applications, and outlook. J Biomed Opt 16:110801 - PubMed
-
- Oldenbourg R (1996) A new view on polarization microscopy. Nature 381:811–812 - PubMed
-
- Das N, Chatterjee S, Soni J, Jagtap J, Pradhan A, Sengupta TK, Panigrahi PK, Vitkin IA, Ghosh N (2013) Probing multifractality in tissue refractive index: prospects for precancer detection. Opt lett 38:211–213 - PubMed
-
- Tuchin VV (2010) Handbook of photonics for biomedical science. CRC Press
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

