Magnetic steering continuum robot for transluminal procedures with programmable shape and functionalities
- PMID: 38704384
- PMCID: PMC11069526
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48058-x
Magnetic steering continuum robot for transluminal procedures with programmable shape and functionalities
Abstract
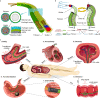
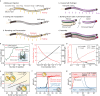
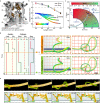
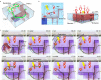
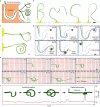
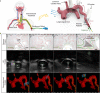
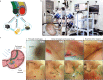
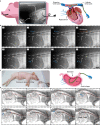
Millimeter-scale soft continuum robots offer safety and adaptability in transluminal procedures due to their passive compliance, but this feature necessitates interactions with surrounding lumina, leading to potential medical risks and restricted mobility. Here, we introduce a millimeter-scale continuum robot, enabling apical extension while maintaining structural stability. Utilizing phase transition components, the robot executes cycles of tip-based elongation, steered accurately through programmable magnetic fields. Each motion cycle features a solid-like backbone for stability, and a liquid-like component for advancement, thereby enabling autonomous shaping without reliance on environmental interactions. Together with clinical imaging technologies, we demonstrate the capability of navigating through tortuous and fragile lumina to transport microsurgical tools. Once it reaches larger anatomical spaces such as stomach, it can morph into functional 3D structures that serve as surgical tools or sensing units, overcoming the constraints of initially narrow pathways. By leveraging this design paradigm, we anticipate enhanced safety, multi-functionality, and cooperative capabilities among millimeter-scale continuum robots, opening new avenues for transluminal robotic surgery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preliminary study on magnetic tracking-based planar shape sensing and navigation for flexible surgical robots in transoral surgery: methods and phantom experiments.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2018 Feb;13(2):241-251. doi: 10.1007/s11548-017-1672-8. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2018. PMID: 28983750
-
Ferromagnetic soft continuum robots.Sci Robot. 2019 Aug 28;4(33):eaax7329. doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.aax7329. Sci Robot. 2019. PMID: 33137788
-
Surgical robots for SPL and NOTES: a review.Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2015 Feb;24(1):8-17. doi: 10.3109/13645706.2014.999687. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2015. PMID: 25597629 Review.
-
Shape Sensing Techniques for Continuum Robots in Minimally Invasive Surgery: A Survey.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2017 Aug;64(8):1665-1678. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2016.2622361. Epub 2016 Oct 27. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 27810796 Review.
-
Design and Development of a Growing Pneumatic Soft Robot.Soft Robot. 2020 Aug;7(4):521-533. doi: 10.1089/soro.2019.0083. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Soft Robot. 2020. PMID: 32150509
Cited by
-
Advances in Magnetically Controlled Medical Robotics: A Review of Actuation Systems, Continuum Designs, and Clinical Prospects for Minimally Invasive Therapies.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 May 6;16(5):561. doi: 10.3390/mi16050561. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the structural function and motion performance of pneumatic flexible tree-climbing robot.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 11;20(6):e0323335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323335. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40498696 Free PMC article.
-
Water-Induced Shape-Locking Magnetic Robots.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(36):e2405021. doi: 10.1002/advs.202405021. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39073727 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional Magnetic Catheter Robot with Triaxial Force Sensing Capability for Minimally Invasive Surgery.Research (Wash D C). 2025 Apr 24;8:0681. doi: 10.34133/research.0681. eCollection 2025. Research (Wash D C). 2025. PMID: 40276100 Free PMC article.
-
Stretchable, Multiplexed, and Bimodal Sensing Electronic Armor for Colonoscopic Continuum Robot Enhanced by Triboelectric Artificial Synapse.Adv Mater. 2025 Aug;37(33):e2502203. doi: 10.1002/adma.202502203. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40474423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cianchetti M, Laschi C, Menciassi A, Dario P. Biomedical applications of soft robotics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018;3:143–153. doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0022-y. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

