Chromosome-level genome assembly of Odontothrips loti Haliday (Thysanoptera: Thripidae)
- PMID: 38704405
- PMCID: PMC11069530
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-024-03289-x
Chromosome-level genome assembly of Odontothrips loti Haliday (Thysanoptera: Thripidae)
Abstract
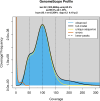
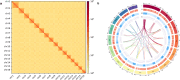
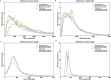
As the predominant pest of alfalfa, Odontothrips loti Haliday causes great damages over the major alfalfa-growing regions of China. The characteristics of strong mobility and fecundity make them develop rapidly in the field and hard to be controlled. There is a shortage of bioinformation and limited genomic resources available of O. loti for us to develop novel pest management strategies. In this study, we constructed a chromosome-level reference genome assembly of O. loti with a genome size of 346.59 Mb and scaffold N50 length of 18.52 Mb, anchored onto 16 chromosomes and contained 20128 genes, of which 93.59% were functionally annotated. The results of 99.20% complete insecta_odb10 genes in BUSCO analysis, 91.11% short reads mapped to the ref-genome, and the consistent tendency among the thrips in the distribution of gene length reflects the quality of genome. Our study provided the first report of genome for the genus Odontothrips, which offers a genomic resource for further investigations on evolution and molecular biology of O. loti, contributing to pest management.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chromosome-level genome assembly of cotton thrips Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera: Thripidae).Sci Data. 2024 Sep 16;11(1):1003. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03737-8. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 39294155 Free PMC article.
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of Odontothrips loti (Haliday, 1852) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019 Dec 9;5(1):7-8. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1693296. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019. PMID: 33366396 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-level genome assembly of bean flower thrips Megalurothrips usitatus (Thysanoptera: Thripidae).Sci Data. 2023 May 3;10(1):252. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02164-5. Sci Data. 2023. PMID: 37137922 Free PMC article.
-
Antennal Transcriptome Analysis of Olfactory Genes and Characterization of Odorant Binding Proteins in Odontothrips loti (Thysanoptera: Thripidae).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 9;24(6):5284. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065284. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982358 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-level genome assembly of the western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis.Sci Data. 2024 Jun 4;11(1):582. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03438-2. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38834623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buhe T, Wang X. Breeding research of the variety of anti-thrips alfalfa. Multifunctional Grasslands In A Changing World, Volume Ii Xxi International Grassland Congress And Viii International Rangeland Congress, Hohhot, China. 2008;29 E 5 Y:5–5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

