Efficacy and Safety of the Melphalan/Hepatic Delivery System in Patients with Unresectable Metastatic Uveal Melanoma: Results from an Open-Label, Single-Arm, Multicenter Phase 3 Study
- PMID: 38704501
- PMCID: PMC11249544
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-024-15293-x
Efficacy and Safety of the Melphalan/Hepatic Delivery System in Patients with Unresectable Metastatic Uveal Melanoma: Results from an Open-Label, Single-Arm, Multicenter Phase 3 Study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Efficacy and Safety of the Melphalan/Hepatic Delivery System in Patients with Unresectable Metastatic Uveal Melanoma: Results from an Open-Label, Single-Arm, Multicenter Phase 3 Study.Ann Surg Oncol. 2024 Nov;31(12):8262-8263. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-15886-6. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39026142 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Uveal melanoma (UM) has a poor prognosis once liver metastases occur. The melphalan/Hepatic Delivery System (melphalan/HDS) is a drug/device combination used for liver-directed treatment of metastatic UM (mUM) patients. The purpose of the FOCUS study was to assess the efficacy and safety of melphalan/HDS in patients with unresectable mUM.
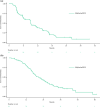
Methods: Eligible patients with mUM received treatment with melphalan (3.0 mg/kg ideal body weight) once every 6 to 8 weeks for a maximum of six cycles. The primary end point was the objective response rate (ORR). The secondary end points included duration of response (DOR), overall survival (OS), and progression-free survival (PFS).
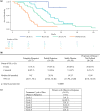
Results: The study enrolled 102 patients with mUM. Treatment was attempted in 95 patients, and 91 patients received treatment. In the treated population (n = 91), the ORR was 36.3 % (95 % confidence interval [CI], 26.44-47.01), including 7.7 % of patients with a complete response. Thus, the study met its primary end point because the lower bound of the 95 % CI for ORR exceeded the upper bound (8.3 %) from the benchmark meta-analysis. The median DOR was 14 months, and the median OS was 20.5 months, with an OS of 80 % at 1 year. The median PFS was 9 months, with a PFS of 65 % at 6 months. The most common serious treatment-emergent adverse events were thrombocytopenia (15.8 %) and neutropenia (10.5 %), treated mostly on an outpatient basis with observation. No treatment-related deaths were observed.
Conclusion: Treatment with melphalan/HDS provides a clinically meaningful response rate and demonstrates a favorable benefit-risk profile in patients with unresectable mUM (study funded by Delcath; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02678572; EudraCT no. 2015-000417-44).
© 2024. Society of Surgical Oncology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

