The Relationship Between Fracture and Mortality in a Chinese Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients Cohort
- PMID: 38706503
- PMCID: PMC11070156
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S457193
The Relationship Between Fracture and Mortality in a Chinese Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients Cohort
Abstract
Background: Patients on maintenance hemodialysis have an increased risk of fracture. However, the relationship between fracture and poor prognosis is not clear.
Methods: A total of 182 maintenance hemodialysis patients were enrolled in the study. The relationship between fracture and poor prognosis (cardiovascular events, stroke, malignancy and 5-year all-cause mortality) were analyzed.
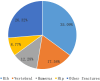
Results: 21 of 182 patients had a history of fracture at the time of enrollment. 26 patients had a new fracture after enrollment. A total of 57 fractures occurred in 47 patients, the most common fracture site was the rib. Patients with fracture group had a higher proportion of elderly and female, higher serum phosphorus and B-type natriuretic peptide and lower hemoglobin, albumin, and potassium compared with those without fracture. Age (OR=3.809, 95% CI: 1.064-8.966, p=0.038), hemoglobin (OR=0.961, 95% CI: 0.925-0.997, p=0.035), and serum phosphorus (OR=3.325, 95% CI:1.104-10.019, p=0.033) were the independent risk factors of new fractures in MHD patients. The incidence of malignancy and 5-year all-cause mortality in patients with fracture was higher than those without fracture (p<0.05). But there was no significant difference in the incidence of acute myocardial infarction or stroke.
Conclusion: 25.8% of maintenance hemodialysis patients had at least one fracture, with rib fractures accounting for the highest proportion. Age, hemoglobin and serum phosphorus were the independent risk factors of new fractures. The incidence of malignancy and 5-year all-cause mortality in patients with fracture was higher than those without fracture, but there was no significant difference in the incidence of acute myocardial infarction and stroke.
Keywords: anemia; fracture; hemodialysis; hyperphosphatemia; mortality.
Plain language summary
To determine the incidence of fractures in hemodialysis patients, we conducted this single center, prospective observational study. 182 patients were enrolled. We also recorded the 5-year incidence of acute myocardial infarction(AMI), stroke, malignancy, and mortality. Our results showed that the incidence of fracture in hemodialysis patients was 25.8%. The most common fracture site was the rib. There were significant statistical differences in age, gender, hemoglobin, serum albumin, B-type natriuretic peptide, potassium and phosphorus between patients with and without fractures. Logistic regression analysis suggested that advanced age, anaemia and hyperphosphatemia were independent risk factors for new fractures in hemodialysis patients. We followed 182 patients for 5 years and recorded the incidence of stroke, AMI and malignancy. The rates of AMI and stroke did not differ significantly between the two groups. However, the incidence of malignancy in patients with fractures is significantly higher than that in patients without fractures. In our study, a total of 74 patients died, including 24 deaths in the fracture group and 50 deaths in the non-fracture group. The main causes of death in 74 cases were cardiovascular events. Our study provides some insight into the association between fractures and poor outcomes in hemodialysis patients.
© 2024 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, or publication of this manuscript.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

