Using Inspiratory Muscle Training to Improve Respiratory Strength, Functional Capacity, Fatigue, and Stress in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Surgery
- PMID: 38706507
- PMCID: PMC11070168
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S463961
Using Inspiratory Muscle Training to Improve Respiratory Strength, Functional Capacity, Fatigue, and Stress in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Surgery
Abstract
Purpose: The main aim of the trial was to assess the effectiveness of inspiratory muscle training on respiratory muscle strength, functional capacity, fatigue, and stress in post-surgical breast cancer survivors.
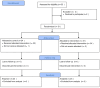
Methods: Forty-seven females who had undergone unilateral post-mastectomy were randomly assigned to an intervention group (IG; n = 24) and a control group (CG; n = 23). Both groups received aerobic exercise training. In addition, the intervention group received inspiratory muscle training 3 days a week for 8 weeks. Maximum inspiratory and expiratory pressure (Pimax) (Pemex), 6-minute walk test, Handgrip strength by hand-held dynamometer, Fatigue Assessment Scale (FAS), and Perceived Stress Scale pss 10 values were measured before the training and then at the eighth week for both groups.
Results: No differences were detected between the groups in terms of sample and clinical characteristics 8 weeks post-intervention. In favor of the intervention group, a significant difference with medium to high effect size was found in terms of Pimax, Pemax, FAS, PS, and 6MWT (p < 0.05). However, there was no difference in terms of handgrip strength (p-value: 0.072), with a medium effect size (0.070). Regarding within-group comparisons, IG exhibited substantial differences in all outcome measures (p < 0.05) compared to CG, with the exception of PImax and 6MWT.
Conclusion: In post-operative breast cancer survivors, respiratory muscle training combined with aerobic training increases respiratory muscle strength and functional ability while lowering stress and tiredness.
Keywords: aerobic exercises; breathing muscles; function; mastectomy.
© 2024 Ibrahim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Similar articles
-
A six-week inspiratory muscle training and aerobic exercise improves respiratory muscle strength and exercise capacity in lung cancer patients after video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: A randomized controlled trial.Clin Rehabil. 2021 Jun;35(6):840-850. doi: 10.1177/0269215520980138. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Clin Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 33307766 Clinical Trial.
-
A combined inspiratory and expiratory muscle training program improves respiratory muscle strength and fatigue in multiple sclerosis.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013 Oct;94(10):1964-70. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 May 25. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013. PMID: 23714277 Clinical Trial.
-
Inspiratory muscle training at sea level improves the strength of inspiratory muscles during load carriage in cold-hypoxia.Ergonomics. 2020 Dec;63(12):1584-1598. doi: 10.1080/00140139.2020.1807613. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Ergonomics. 2020. PMID: 32812837
-
Respiratory muscle training in children and adults with neuromuscular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 5;9(9):CD011711. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011711.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31487757 Free PMC article.
-
Inspiratory muscle training improves respiratory muscle strength, functional capacity and quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review.J Physiother. 2017 Apr;63(2):76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2017.02.016. Epub 2017 Mar 14. J Physiother. 2017. PMID: 28433237
Cited by
-
Respiratory muscle training reduces painful swallowing and opioid use during radiation therapy for head and neck cancer: a matched pair analysis.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 12;25(1):442. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13756-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40075332 Free PMC article.
-
Using Virtual Reality Pablo Gaming in the Post-Operative Rehabilitation of Breast Cancer Patients: Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 13;13(24):7609. doi: 10.3390/jcm13247609. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39768532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kang JJ, Lee H, Park BH, et al. Efficacy of a 4-Week Nurse-Led Exercise Rehabilitation Program in Improving the Quality of Life in Women Receiving a Post-Mastectomy Reconstruction Using the Motiva ErgonomixTM Round SilkSurface. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;20(1):16. doi:10.3390/ijerph20010016 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous