From 60% to 5% in 12 Weeks: A Trastuzumab-Induced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Drop
- PMID: 38707046
- PMCID: PMC11065541
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.59172
From 60% to 5% in 12 Weeks: A Trastuzumab-Induced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Drop
Abstract
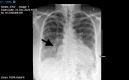
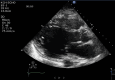
Trastuzumab is the first-line therapy for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer. However, trastuzumab is associated with cardiotoxicity. It manifests with an asymptomatic reduction of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and is reversible after discontinuation. Trastuzumab-induced new-onset acute decompensated heart failure is rare (0.5%). We report a case of a 54-year-old woman who received anthracycline (idarubicin, accumulated dose 400 mg/m2 doxorubicin equivalent) for her acute promyelocytic leukocyte 10 years ago, had no relevant comorbidities or other pre-existing cardiovascular diseases, had maintained normal cardiac function, presenting with new-onset dyspnea at rest and bilateral lower extremities swelling 12 weeks after receiving trastuzumab induction chemotherapy for her newly diagnosed early stage HER2-positive breast cancer. Chest X-ray showed severe pulmonary edema. Echocardiography revealed diffuse left ventricular hypokinesis with LVEF 5%. After other possible etiology of cardiomyopathy, including ischemia, infection, substance, or radiation, were excluded by extensive cardiomyopathy workup, a diagnosis of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity was established. Trastuzumab was discontinued, and the patient's symptom was improved with furosemide. Guildline-directed medical therapy was gradually maximized over three months. Repeat transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) at one-year follow-up after the initial diagnosis shows LVEF 33%, and the patient was referred to an advanced heart failure clinic. This case report demonstrated a rare catastrophic cardiac toxicity effect of trastuzumab and its potential association with remote exposure to anthracycline. Studies have investigated the cardiotoxicity in the concurrent use of trastuzumab and anthracycline therapy. However, how trastuzumab affected patients who were exposed to anthracycline for more than eight years had remained unreported. To our knowledge, no previous detailed case report has described the same clinical scenario as in this case. The case also demonstrates the limitation of the commonly used cardio-oncology cardiovascular risk assessment tool and highlights the importance of individualized cardiovascular risk stratification when deciding on chemotherapy plans.
Keywords: anthracycline; breast cancer; cardiotoxicity; congestive heart failure; trastuzumab.
Copyright © 2024, Pan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: a review of clinical risk factors, pharmacologic prevention, and cardiotoxicity of other HER2-directed therapies.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jul;188(1):21-36. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06280-x. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34115243 Review.
-
Trastuzumab in Female Breast Cancer Patients With Reduced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Aug 7;7(15):e008637. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008637. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 30371238 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac outcomes of trastuzumab therapy in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 May;175(1):239-246. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05139-6. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30721443 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac safety of non-anthracycline trastuzumab-based therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Nov;166(1):241-247. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4362-x. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 28710537 Free PMC article.
-
Left Ventricular Dysfunction With Trastuzumab Therapy: Is Primary Prevention the Best Option?J Clin Oncol. 2017 Mar 10;35(8):820-825. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.71.0038. Epub 2016 Dec 28. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28029315 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of early cardiotoxicity in HER2-positive breast cancer patients receiving radiotherapy and concurrent trastuzumab.Ir J Med Sci. 2025 Feb;194(1):7-18. doi: 10.1007/s11845-024-03835-x. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Ir J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39495473
References
-
- 2016 ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: the Task Force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez Muñoz D, et al. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2768–2801. - PubMed
-
- Cardiotoxicity of anticancer treatments: what the cardiologist needs to know. Ewer MS, Ewer SM. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010;7:564–575. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
