Comparison of Effectiveness and Safety of Apixaban, Dabigatran, and Rivaroxaban in Patients With Valvular Atrial Fibrillation: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized-Control Trials and Observational Studies
- PMID: 38707166
- PMCID: PMC11070143
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.57656
Comparison of Effectiveness and Safety of Apixaban, Dabigatran, and Rivaroxaban in Patients With Valvular Atrial Fibrillation: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized-Control Trials and Observational Studies
Abstract
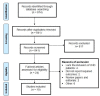
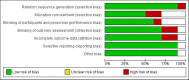
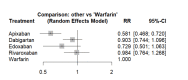
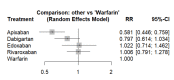
The objective of this network meta-analysis was to assess the efficacy and safety of apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and edoxaban in patients diagnosed with atrial fibrillation and valvular heart disease. A comprehensive search was conducted across various electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science, from inception to February 15, 2024. The search strategy utilized a combination of medical subject headings (MeSH) terms and relevant keywords related to valvular heart disease, atrial fibrillation, anticoagulant therapy, and study design, such as randomized controlled trials and observational studies. The outcomes evaluated in this analysis comprised the incidence of stroke or systemic embolism (SE), as well as the occurrences of major bleeding events. A total of 10 studies were incorporated into this meta-analysis, encompassing 40,662 participants. Of these, 12,385 received apixaban, 2,829 received dabigatran, 13,662 received rivaroxaban, 2,582 received edoxaban, and 9,202 received warfarin. The duration of follow-up in the included studies ranged from 3 to 54 months. Among the four direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) studied, apixaban demonstrated a significant reduction in the risk of stroke or SE when compared to other DOACs and warfarin, highlighting its efficacy in patients with atrial fibrillation and valvular heart disease. Additionally, apixaban exhibited a lower risk of major bleeding events, further emphasizing its favorable safety profile compared to the other agents assessed. In conclusion, our findings suggest that apixaban may be more effective and safer than other DOACs and warfarin in this patient population. However, additional studies are warranted to compare the various DOACs in this cohort to identify the optimal treatment strategy for preventing adverse outcomes.
Keywords: apixaban; dabigartan; rivaroxaban; systematic review and meta-analysis; valvular atrial fibrillation.
Copyright © 2024, Huma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:373–498. - PubMed
-
- Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, et al. Lancet. 2014;383:955–962. - PubMed
-
- Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, et al. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:981–992. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
