Quantifying the dose-response relationship between exercise and health-related quality of life in patients undergoing haemodialysis: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 38707251
- PMCID: PMC11066687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2024.102737
Quantifying the dose-response relationship between exercise and health-related quality of life in patients undergoing haemodialysis: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This meta-analysis aims to explore the dose-response relationship of aerobic exercise or aerobic combined resistance exercise on cardiopulmonary function in maintenance hemodialysis(MHD), with the goal of aiding in the formulation of precise exercise prescriptions.
Methods: A literature search up to August 18, 2023, was conducted in databases including Web of Science, among others, focusing on the effects of exercise interventions on cardiopulmonary function in hemodialysis patients.Two researchers independently conducted literature screening, data extraction, and an assessment of study methodology quality. A dose-response meta-analysis was carried out using a one-stage cubic spline mixed-effects model, followed by stratified analyses based on intervention period, intervention method, and exercise environment.
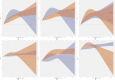
Results: A nonlinear dose-response relationship was observed between exercise and 6-minute walk test (6WMT) as well as peak oxygen uptake (VO2Peak) in hemodialysis patients. The optimal exercise dose for the 6WMT across the full exposure range was 922 METs-min/week, with VO2Peak increasing with the dose. The effects were influenced by the type of exercise, intervention period, and exercise environment. An exercise dose of 500 METs-min/week and 619 METs-min/week was found sufficient to achieve the minimal clinically important differences (MCID) for 6WMT and VO2Peak, respectively.
Conclusion: There is a significant association between the dose of exercise and its effects. With appropriate adjustment of variables, even low-dose exercise can lead to clinically significant improvements in cardiopulmonary function.
Keywords: 6 min walking ability; Cardiopulmonary function; Exercise; Hemodialysis; Meta-analysis of dose response; Peak oxygen uptake.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Standard technical specifications for methacholine chloride (Methacholine) bronchial challenge test (2023)].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 12;47(2):101-119. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20231019-00247. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38309959 Chinese.
-
Effects of different rehabilitation modality on cardiopulmonary function in patients with acute coronary syndrome after revascularization.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Mar 4;10:1120665. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1120665. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38500679 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Peak Oxygen Uptake in Bicycle Exercise Test Caused by Body Positions: A Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Oct 11;8:734687. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.734687. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34708089 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
The 2-minute walk test is not a valid method to determine aerobic capacity in persons with Multiple Sclerosis.NeuroRehabilitation. 2019;45(2):239-245. doi: 10.3233/NRE-192792. NeuroRehabilitation. 2019. PMID: 31498142 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prescribing Physical Activity and Exercise for People with CKD: A Practical Guide by the Global Renal Exercise Network.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2025 Mar 14;20(6):876-888. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000708. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40085159 Review.
References
-
- Anastasia S., Evangelia K., Konstantinos F., Serafeim A., Asterios D. The effects of aquatic exercise on functional capacity and health-related quality of life in hemodialysis patients. J Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016;1(15):1–6.
-
- Baria F., Kamimura M.A., Aoike D.T., Ammirati A., Rocha M.L., de Mello M.T., et al. Randomized controlled trial to evaluate the impact of aerobic exercise on visceral fat in overweight chronic kidney disease patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014;29(4):857–864. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft529. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

