The efficacy of low frequency repetitive transcial magnetic stimulation for treating auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia: Insights from functional gradient analyses
- PMID: 38707410
- PMCID: PMC11066630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30194
The efficacy of low frequency repetitive transcial magnetic stimulation for treating auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia: Insights from functional gradient analyses
Abstract
Background: Auditory Verbal Hallucinations (AVH) constitute a prominent feature of schizophrenia. Although low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) has demonstrated therapeutic benefits in ameliorating AVH, the underlying mechanisms of its efficacy necessitate further elucidation.
Objective: This study investigated the cortical gradient characteristics and their associations with clinical responses in schizophrenia patients with AVH, mediated through 1 Hz rTMS targeting the left temporoparietal junction.
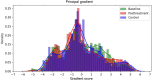
Method: Functional gradient metrics were employed to examine the hierarchy patterns of cortical organization, capturing whole-brain functional connectivity profiles in patients and controls.
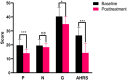
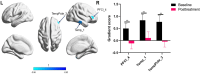
Results: The 1 Hz rTMS treatment effectively ameliorated the positive symptoms in patients, specifically targeting AVH. Initial evaluations revealed expanded global gradient distribution patterns and specific principal gradient variations in certain brain regions in patients at baseline compared to a control cohort. Following treatment, these divergent global and local patterns showed signs of normalizing. Furthermore, there was observed a closer alignment in between-network dispersion among various networks after treatment, including the somatomotor, attention, and limbic networks, indicating a potential harmonization of brain functionality.
Conclusion: Low-frequency rTMS induces alternations in principal functional gradient patterns, may serve as imaging markers to elucidate the mechanisms underpinning the therapeutic efficacy of rTMS on AVH in schizophrenia.
Keywords: Auditory verbal hallucinations; Brain connectivity patterns; Functional gradient; Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; Schizophrenia.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Alterations in brain connectivity patterns in schizophrenia patients with auditory verbal hallucinations during low frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation.Psychiatry Res. 2023 Oct;328:115457. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2023.115457. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Psychiatry Res. 2023. PMID: 37716322
-
Low-frequency rTMS modulates small-world network properties in an AVH-related brain network in schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 15;16:1578072. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1578072. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40303447 Free PMC article.
-
Low-frequency rTMS induces modifications in cortical structural connectivity - functional connectivity coupling in schizophrenia patients with auditory verbal hallucinations.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Feb 15;45(3):e26614. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26614. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38375980 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the efficacy of transcranial magnetic stimulation for auditory verbal hallucinations.Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Jul 15;76(2):101-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.09.038. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24315551 Review.
-
[The use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in auditory verbal hallucinations (AVH)].Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2010 Nov;78(11):632-43. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1245499. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2010. PMID: 20648414 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Targeting auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia: effective connectivity changes induced by low-frequency rTMS.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 28;14(1):393. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-03106-4. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39341819 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- McCutcheon R.A., Reis Marques T., Howes O.D. Schizophrenia—an Overview. JAMA Psychiatr. 2020;77(2):201–210. - PubMed
-
- Cloutier M., et al. The economic burden of schizophrenia in the United States in 2013. J. Clin. Psychiatr. 2016;77(6):764–771. - PubMed
-
- Bauer S.M., et al. Culture and the prevalence of hallucinations in schizophrenia. Compr. Psychiatr. 2011;52(3):319–325. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

