The predictive value of serum tumor markers for EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer patients with non-stage IA
- PMID: 38707478
- PMCID: PMC11066585
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29605
The predictive value of serum tumor markers for EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer patients with non-stage IA
Abstract
Objective: The predictive value of serum tumor markers (STMs) in assessing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations among patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), particularly those with non-stage IA, remains poorly understood. The objective of this study is to construct a predictive model comprising STMs and additional clinical characteristics, aiming to achieve precise prediction of EGFR mutations through noninvasive means.
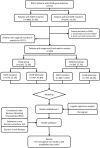
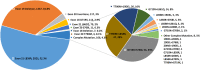
Materials and methods: We retrospectively collected 6711 NSCLC patients who underwent EGFR gene testing. Ultimately, 3221 stage IA patients and 1442 non-stage IA patients were analyzed to evaluate the potential predictive value of several clinical characteristics and STMs for EGFR mutations.
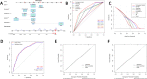
Results: EGFR mutations were detected in 3866 patients (57.9 %) of all NSCLC patients. None of the STMs emerged as significant predictor for predicting EGFR mutations in stage IA patients. Patients with non-stage IA were divided into the study group (n = 1043) and validation group (n = 399). In the study group, univariate analysis revealed significant associations between EGFR mutations and the STMs (carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC), and cytokeratin-19 fragment (CYFRA21-1)). The nomogram incorporating CEA, CYFRA 21-1, pathology, gender, and smoking history for predicting EGFR mutations with non-stage IA was constructed using the results of multivariate analysis. The area under the curve (AUC = 0.780) and decision curve analysis demonstrated favorable predictive performance and clinical utility of nomogram. Additionally, the Random Forest model also demonstrated the highest average C-index of 0.793 among the eight machine learning algorithms, showcasing superior predictive efficiency.
Conclusion: CYFRA21-1 and CEA have been identified as crucial factors for predicting EGFR mutations in non-stage IA NSCLC patients. The nomogram and 8 machine learning models that combined STMs with other clinical factors could effectively predict the probability of EGFR mutations.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Lung cancer; Machine learning; Nomogram model; Serum tumor markers.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Value of serum tumor markers for predicting EGFR mutations and positive ALK expression in 1089 Chinese non-small-cell lung cancer patients: A retrospective analysis.Eur J Cancer. 2020 Jan;124:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.10.005. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Eur J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31707279
-
Identification of EGFR mutation status in male patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: role of 18F-FDG PET/CT and serum tumor markers CYFRA21-1 and SCC-Ag.EJNMMI Res. 2023 Apr 4;13(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13550-023-00976-5. EJNMMI Res. 2023. PMID: 37014455 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic monitoring serum tumor markers to predict molecular features of EGFR-mutated lung cancer during targeted therapy.Cancer Med. 2022 Aug;11(16):3115-3125. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4676. Epub 2022 May 11. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35543090 Free PMC article.
-
Serum tumor markers for response prediction and monitoring of advanced lung cancer: A review focusing on immunotherapy and targeted therapies.Tumour Biol. 2024;46(s1):S233-S268. doi: 10.3233/TUB-220039. Tumour Biol. 2024. PMID: 37248927 Review.
-
Prognostic value of blood-based protein biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer: A critical review and 2008-2022 update.Tumour Biol. 2024;46(s1):S111-S161. doi: 10.3233/TUB-230009. Tumour Biol. 2024. PMID: 37927288 Review.
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Wagle N.S., Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2023;73(1):17–48. 2023. - PubMed
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y., Au J.S., Thongprasert S., Srinivasan S., Tsai C.M., Khoa M.T., Heeroma K., Itoh Y., Cornelio G., Yang P.C. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER) J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014;9(2):154–162. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

