Nootropic effect of Indian Royal Jelly against okadaic acid induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease: Inhibition of neuroinflammation and acetylcholineesterase
- PMID: 38707922
- PMCID: PMC11068996
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.11.005
Nootropic effect of Indian Royal Jelly against okadaic acid induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease: Inhibition of neuroinflammation and acetylcholineesterase
Abstract
Background: Royal jelly is an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective bee product. There are several sources for royal jelly and one of them is Indian Royal Jelly (IRJ). However, the neuroprotective actions of IRJ and the underlying molecular mechanisms involved are not well known.
Objective: To evaluate the neuroprotective effect of IRJ in the okadaic acid (OKA)-induced Alzheimer's disease (AD) model in rats.
Methods: In male Wistar rats, OKA was intracerebroventricularly (ICV) administered, and from day 7, they were treated orally with IRJ or memantine for 21 days. Spatial and recognition learning and memory were evaluated from days 27-34; employing the Morris water maze (MWM) and the novel object recognition tests (NORT), respectively. In vitro biochemical measurements were taken of the cholinergic system and oxidative stress markers. In silico docking was used to find the role of tau protein kinase and phosphatase in the pharmacological action.
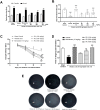
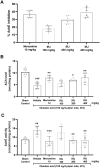
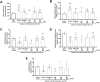
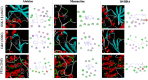
Results: In OKA-induced rats, IRJ decreased the escape latency and path length in MWM and increased the exploration time for novel objects and the discrimination index in NORT. ICV-OKA rats had higher free radicals and cytokines that caused inflammation and their level of free radical scavengers was back to normal with IRJ treatment. IRJ increased the level of acetylcholine and inhibited acetylcholinesterase. Moreover, the in silico docking study revealed the strong binding affinity of 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid (10-HDA), a bioactive constituent of IR, to the tau protein kinases and phosphatases.
Conclusion: IRJ may serve as a nootropic agent in the treatment of dementia, and owing to its capacity to prevent oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, and increase cholinergic tone; it has the potential to be explored as a novel strategy for the treatment of dementia and AD. More studies may be needed to develop 10-HDA as a novel drug entity for AD.
Keywords: 10-Hydroxy-2-decenoic acid; Alzheimer's disease; Indian royal jelly; Neuroinflammation; Okadaic acid; Tau protein kinases.
© 2023 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Rahul N. Dubey, Sathiyanarayanan L, Sandeep Sankaran and Arulmozhi S declare that they have no conflict interests to declare that are relevant to the work reported in this manuscript.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Okadaic acid-induced Tau phosphorylation in rat brain: role of NMDA receptor.Neuroscience. 2013 May 15;238:97-113. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.01.075. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23415789
-
Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on okadaic acid induced memory impairment in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 5;715(1-3):381-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.033. Epub 2013 May 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23685326
-
Sodium orthovanadate improves learning and memory in intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin rat model of Alzheimer's disease through modulation of brain insulin resistance induced tau pathology.Brain Res Bull. 2020 Nov;164:83-97. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Aug 9. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 32784004
-
Royal jelly: a predictive, preventive and personalised strategy for novel treatment options in non-communicable diseases.EPMA J. 2023 Jul 18;14(3):381-404. doi: 10.1007/s13167-023-00330-8. eCollection 2023 Sep. EPMA J. 2023. PMID: 37605655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Profile of Alzheimer's Disease: Is 10-Hydroxy-2-decenoic Acid a Pertinent Metabolic Adjuster?Metabolites. 2023 Aug 18;13(8):954. doi: 10.3390/metabo13080954. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37623897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Royal Jelly Enhances the Social Status of Submissive Rats by Restoring Balance to the Disturbed Gut-Brain Communication.Foods. 2025 Feb 27;14(5):819. doi: 10.3390/foods14050819. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40077522 Free PMC article.
-
Royal jelly acid: preparation, metabolism and therapeutic potential.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 26;16:1561351. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1561351. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40492134 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
