Green synthesis of (R)-3-hydroxy-decanoic acid and analogs from levoglucosenone: a novel access to the fatty acid moiety of rhamnolipids
- PMID: 38708030
- PMCID: PMC11066284
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1362878
Green synthesis of (R)-3-hydroxy-decanoic acid and analogs from levoglucosenone: a novel access to the fatty acid moiety of rhamnolipids
Abstract
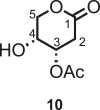
Rhamnolipids (RLs) are highly valuable molecules in the cosmetic, pharmaceutic, and agricultural sectors with outstanding biosurfactant properties. In agriculture, due to their potential to artificially stimulate the natural immune system of crops (also known as elicitation), they could represent a critical substitute to conventional pesticides. However, their current synthesis methods are complex and not aligned with green chemistry principles, posing a challenge for their industrial applications. In addition, their bioproduction is cumbersome with reproducibility issues and expensive downstream processing. This work offers a more straightforward and green access to RLs, crucial to decipher their mechanisms of action and design novel potent and eco-friendly elicitors. To achieve this, we propose an efficient seven-step synthetic pathway toward (R)-3-hydroxyfatty acid chains present in RLs, starting from cellulose-derived levoglucosenone, with Michael addition, Baeyer-Villiger oxidation, Bernet-Vasella reaction, and cross-metathesis homologation as key steps. This method allowed the production of (R)-3-hydroxyfatty acid chains and derivatives with an overall yield ranging from 24% to 36%.
Keywords: Michael addition; crop protection agent; cross-coupling; green chemistry; levoglucosenone.
Copyright © 2024 Petracco, Flourat, Belhomme, Castex, Brunissen, Brunois, Peru, Allais and Haudrechy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures





References
-
- Allais F., Bonneau G., Peru A. A. M., Flourat A. L. (2018). Method for converting levoglucosenone into 4-hydroxymethyl butyrolactone or 4-hydroxymethyl butenolide without using any organic solvent and catalyst. https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2018007764A1/en.
-
- Aspinall G. O., Chatterjee D., Khondo L. (1984). The hex-5-enose degradation: zinc dust cleavage of 6-Deoxy-6-Iodo-a-D-Galactopyranosidic linkages in methylated di- and trisaccharides. Can. J. Chem. 62, 2728–2735. 10.1139/v84-464 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

