Nephroprotective Effect of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Leaf Flavonoid Extracts via KIM-1 and TGF-1β Signaling Pathways in Streptozotocin-Induced Rats
- PMID: 38708257
- PMCID: PMC11064007
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00254
Nephroprotective Effect of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Leaf Flavonoid Extracts via KIM-1 and TGF-1β Signaling Pathways in Streptozotocin-Induced Rats
Abstract
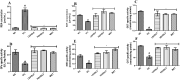
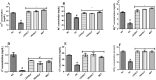
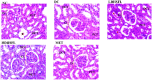
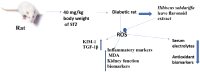
Diabetes-induced kidney damage represents a substantial health hazard, emphasizing the imperative to explore potential therapeutic interventions. This study investigates the nephroprotective activity of flavonoid-rich extracts from Hibiscus sabdariffa leaves in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The flavonoid-rich extracts of H. sabdariffa leaves was obtained using a standard procedure. The animals were induced with streptozotocin and thereafter treated with both low (LDHSFL) and high doses (HDHSFL) of flavonoid-rich extracts from H. sabdariffa leaves and metformin (MET), and other groups are diabetic control (DC) and normal control (NC). The study assesses diverse renal parameters, encompassing kidney redox stress biomarkers, serum electrolyte levels, kidney inflammatory biomarkers, serum concentrations of creatinine, urea, and uric acid, kidney phosphatase activities, renal histopathology, and relative gene expressions of kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) and transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-1β), comparing these measurements with normal and diabetic control groups (NC and DC). The findings indicate that the use of extracts from H. sabdariffa leaves markedly (p < 0.05) enhanced renal well-being by mitigating nephropathy, as demonstrated through the adjustment of various biochemical and gene expression biomarkers, indicating a pronounced antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effect, improved kidney morphology, and mitigation of renal dysfunction. These findings suggest that H. sabdariffa leaf flavonoid extracts exhibit nephroprotective properties, presenting a potential natural therapeutic approach for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Nephroprotective Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa Leaf and Ellagic Acid in Vitro and in Vivo Models of Hyperuricemic Nephropathy.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Jan 11;71(1):382-397. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c05720. Epub 2022 Dec 23. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36562602
-
Hibiscus sabdariffa renews pancreatic β-cells in experimental type 1 diabetic model rats.Morphologie. 2019 Jun;103(341 Pt 2):80-93. doi: 10.1016/j.morpho.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 May 15. Morphologie. 2019. PMID: 31101500
-
Anti-hepatotoxic activities of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. in animal model of streptozotocin diabetes-induced liver damage.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jul 30;14:277. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-277. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25077880 Free PMC article.
-
Chemopreventive properties and molecular mechanisms of the bioactive compounds in Hibiscus sabdariffa Linne.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(8):1245-54. doi: 10.2174/092986711795029663. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21291361 Review.
-
Phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological aspects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L.: a review.Phytother Res. 2005 May;19(5):369-75. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1628. Phytother Res. 2005. PMID: 16106391 Review.
Cited by
-
Obacunone inhibits ferroptosis through regulation of Nrf2 homeostasis to treat diabetic nephropathy.Mol Med Rep. 2025 May;31(5):135. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13500. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40116089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodríguez-Fierros F. L.; Guarner-Lans V.; Soto M. E.; Manzano-Pech L.; Díaz-Díaz E.; Soria-Castro E.; Rubio-Ruiz M. E.; Jiménez-Trejo F.; Pérez-Torres I. Modulation of renal function in a metabolic syndrome rat model by antioxidants in Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Molecules 2021, 26 (7), 2074.10.3390/molecules26072074. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jamshidi-Kia F.; Lorigooini Z.; Amini-Khoei H. Medicinal plants: Past history and future perspective. J. HerbMed Pharmacol. 2018, 7 (1), 1–7. 10.15171/jhp.2018.01. - DOI
-
- Gunjan M.; Naing T. W.; Saini R. S.; Ahmad A.; Naidu J. R.; Kumar I. Marketing trends & future prospects of herbal medicine in the treatment of various disease. World J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 4 (9), 132–155.
-
- Faujdar C., Priyadarshini. Natural Compounds Extracted from Medicinal Plants and Their Applications in Cardiovascular and Kidney Diseases. Nat. Bioact. Compd. 2019, 297–312.. 10.1007/978-981-13-7205-6_13. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
