Bedside clinical assessment of patients with common upper limb tremor and algorithmic approach
- PMID: 38708334
- PMCID: PMC11063083
- DOI: 10.2478/abm-2024-0008
Bedside clinical assessment of patients with common upper limb tremor and algorithmic approach
Abstract
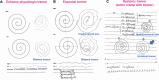
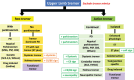
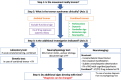
The diagnostic approach for patients with tremor is challenging due to the complex and overlapping phenotypes among tremor syndromes. The first step in the evaluation of tremor is to identify the tremulous movement and exclude the tremor mimics. The second step is to classify the tremor syndrome based on the characteristics of tremor from historical clues and focused examination (Axis 1). Comprehensive tremor examinations involve the assessment of tremor in different conditions (rest, action or mixed, position or task-specific), distribution of tremor (upper limb, lower limb, head, jaw), positive signs for functional tremor (FT) if suspected (distractibility, entrainment, co-contraction), and associated neurological signs including parkinsonism, dystonic posture, cerebellar/brainstem signs, neuropathy, and cognitive impairment. A pivotal feature in this step is to determine any distinct feature of a specific isolated or combined tremor syndrome. In this review, we propose an algorithm to assess upper limb tremors. Ancillary testing should be performed if clinical evaluation is unclear. The choice of investigation depends on the types of tremors considered to narrow down the spectrum of etiology (Axis 2). Laboratory blood tests are considered for acute onset and acute worsening of tremors, while structural neuroimaging is indicated in unilateral tremors with acute onset, nonclassical presentations, and a combination of neurological symptoms. Neurophysiological study is an important tool that aids in distinguishing between tremor and myoclonus, etiology of tremor and document specific signs of FT. Treatment is mainly symptomatic based depending on the etiology of the tremor and the patient's disabilities.
Keywords: clinical assessment; investigations; neurophysiology; tremor; upper limb tremor.
© 2024 Pattamon Panyakaew et al., published by Sciendo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic clinical approach for diagnosing upper limb tremor.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Aug;91(8):822-830. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2019-322676. Epub 2020 May 26. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32457087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is essential tremor a family of diseases or a syndrome? A syndrome.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2022;163:31-59. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2022.02.002. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35750367
-
Utility of tremor electrophysiology studies.Clin Park Relat Disord. 2021 Sep 24;5:100108. doi: 10.1016/j.prdoa.2021.100108. eCollection 2021. Clin Park Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 34632367 Free PMC article.
-
Do We Belittle Essential Tremor by Calling It a Syndrome Rather Than a Disease? No.Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 30;11:586606. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.586606. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33101188 Free PMC article.
-
The role of laboratory investigations in the classification of tremors.Neurol Sci. 2023 Dec;44(12):4183-4192. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-07108-w. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37814130 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical utility of synuclein skin biopsy in the diagnosis and evaluation of synucleinopathies.Front Neurol. 2024 Dec 18;15:1510796. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1510796. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39744104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Louis ED. Tremor. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2019;25:959–75. - PubMed
-
- Louis ED, Ferreira JJ. How common is the most common adult movement disorder? Update on the worldwide prevalence of essential tremor. Mov Disord. 2010;25:534–41. - PubMed
-
- Lee A, Sarva H. Approach to tremor disorders. Semin Neurol. 2021;41:731–43. - PubMed
-
- Marsili L, Bologna M, Mahajan A. Diagnostic uncertainties in tremor. Semin Neurol. 2023;43:156–65. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
