Improvement of morphophysiological and anatomical attributes of plants under abiotic stress conditions using plant growth-promoting bacteria and safety treatments
- PMID: 38708356
- PMCID: PMC11067897
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17286
Improvement of morphophysiological and anatomical attributes of plants under abiotic stress conditions using plant growth-promoting bacteria and safety treatments
Abstract
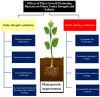
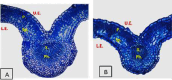
Drought and salinity are the major abiotic stress factors negatively affecting the morphophysiological, biochemical, and anatomical characteristics of numerous plant species worldwide. The detrimental effects of these environmental factors can be seen in leaf and stem anatomical structures including the decrease in thickness of cell walls, palisade and spongy tissue, phloem and xylem tissue. Also, the disintegration of grana staking, and an increase in the size of mitochondria were observed under salinity and drought conditions. Drought and salt stresses can significantly decrease plant height, number of leaves and branches, leaf area, fresh and dry weight, or plant relative water content (RWC%) and concentration of photosynthetic pigments. On the other hand, stress-induced lipid peroxidation and malondialdehyde (MDA) production, electrolyte leakage (EL%), and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) can increase under salinity and drought conditions. Antioxidant defense systems such as catalase, peroxidase, glutathione reductase, ascorbic acid, and gamma-aminobutyric acid are essential components under drought and salt stresses to protect the plant organelles from oxidative damage caused by ROS. The application of safe and eco-friendly treatments is a very important strategy to overcome the adverse effects of drought and salinity on the growth characteristics and yield of plants. It is shown that treatments with plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) can improve morphoanatomical characteristics under salinity and drought stress. It is also shown that yeast extract, mannitol, proline, melatonin, silicon, chitosan, α-Tocopherols (vitamin E), and biochar alleviate the negative effects of drought and salinity stresses through the ROS scavenging resulting in the improvement of plant attributes and yield of the stressed plants. This review discusses the role of safety and eco-friendly treatments in alleviating the harmful effects of salinity and drought associated with the improvement of the anatomical, morphophysiological, and biochemical features in plants.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; Drought; Economic plants; PGPB; ROS; Salinity.
©2024 Alshammari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Diaa Abd El Moneim is an Academic Editor for PeerJ.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelaal Kh. Effect of salicylic acid and abscisic acid on morpho-physiological and anatomical characters of faba bean plants (Vicia faba L.) under drought stress. Journal of Plant Production. 2015a;6(11):1771–1788. doi: 10.21608/jpp.2015.52096. - DOI
-
- Abdelaal Kh. Pivotal role of bio and mineral fertilizer combinations on morphological anatomical and yield characters of sugar beet plant (Beta vulgaris L.) Middle East Journal of Agriculture Research. 2015b;4(4):717–734.
-
- Abdelaal Kh, Alamrey S, Attia K, Elrobh M, Elnahhas N, Abou El-Yazied A, Ibrahim M. The pivotal role of biochar in enhancement soil properties, morphophysiological and yield characters of barley plants under drought stress. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca. 2022b;50(2):12710. doi: 10.15835/nbha50212710. - DOI
-
- Abdelaal K, Alsubeie MS, Hafez Y, Emeran A, Moghanm F, Okasha S, Omara R, Basahi MA, Darwish DBE, Ibrahim MFM, Abou El-Yazied A, Rashwan E, Elkelish A, Mady M, Ibraheem F. Physiological and biochemical changes in vegetable and field crops under drought, salinity and weeds stresses: control strategies and management. Agriculture. 2022a;12:2084. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12122084. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

