Pan-Cancer Interrogation of B7-H3 (CD276) as an Actionable Therapeutic Target Across Human Malignancies
- PMID: 38709075
- PMCID: PMC11138391
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0546
Pan-Cancer Interrogation of B7-H3 (CD276) as an Actionable Therapeutic Target Across Human Malignancies
Abstract
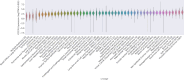
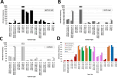
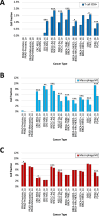
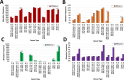
B7-H3 (CD276) is a transmembrane glycoprotein of the B7 immune checkpoint superfamily that has emerged as a promising therapeutic target. To better understand the applicability of B7-H3-directed therapies, we analyzed 156,791 samples comprising 50 cancer types to interrogate the clinical, genomic, transcriptomic, and immunologic correlates of B7-H3 mRNA expression. DNA (592-gene/whole-exome) and RNA (whole-transcriptome) sequencing was performed from samples submitted to Caris Life Sciences. B7-H3 high versus low expression was based on top and bottom quartiles for each cancer type. Patients' overall survival was determined from insurance claims data. Pathway analysis was performed using gene set enrichment analyses. Immune cell fractions were inferred using quanTIseq. B7-H3 is expressed across several human malignancies including prostate, pancreatic, ovarian, and lung cancers. High B7-H3 expression is associated with differences in overall survival, possibly indicating a prognostic role of B7-H3 for some cancers. When examining molecular features across all cancer types, we did not identify recurrent associations between B7-H3 expression and genetic alterations in TP53, RB1, and KRAS. However, we find consistent enrichment of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, Wnt, TGFβ, and Notch signaling pathways. In addition, tumors with high B7-H3 expression are associated with greater proportions of M1 macrophages, but lower fractions of CD8+ T cells. We have begun to define the genomic, transcriptomic, clinical, and immunologic features associated with B7-H3 expression in 50 cancer types. We report novel clinical and molecular features of B7-H3-high tumors which may inform how current B7-H3 therapeutics should be deployed and prioritized.
Significance: B7-H3-targeting therapeutics have shown promising results in initial clinical trials. In this pan-cancer analysis of B7-H3 mRNA expression, we found that B7-H3 exhibits robust expression in many common cancer types. These results may inform further development of B7-H3-targeting therapeutics and may guide clinical decisions for patients with limited treatment options.
© 2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


References
-
- Scribner JA, Brown JG, Son T, Chiechi M, Li P, Sharma S, et al. . Preclinical development of MGC018, a duocarmycin-based antibody–drug conjugate targeting B7-H3 for solid cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2020;19:2235–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA270539/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA077598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA065493/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- W81XWH-22-1-0242/U.S. Department of Defense (DOD)
- R37 R37CA288972-01/HHS | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- University of Minnesota Institute for Prostate and Urologic Cancers Philanthropic Fund
- Randy Shaver Community Cancer Fund
- R35 CA197292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Prostate Cancer Foundation (PCF)
- American Society of Hematology (ASH)
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA111412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008244/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- W81XWH-22-2-0025/U.S. Department of Defense (DOD)
- R35 CA283892/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA288972/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

