Drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis among Nepalese patients at a tuberculosis referral center
- PMID: 38709710
- PMCID: PMC11073693
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301210
Drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis among Nepalese patients at a tuberculosis referral center
Abstract
Background: Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), characterized by isoniazid and rifampicin resistance, is caused by chromosomal mutations that restrict treatment options and complicate tuberculosis management. This study sought to investigate the prevalence of pre-extensively drug-resistant (pre-XDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) tuberculosis, as well as mutation pattern, in Nepalese patients with MDR/rifampicin-resistant (RR)-TB strains.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted on MDR/RR-TB patients at the German Nepal Tuberculosis Project from June 2017 to June 2018. The MTBDRsl line probe assay identified pre-XDR-TB and XDR-TB. Pre-XDR-TB included MDR/RR-TB with resistance to any fluoroquinolone (FLQ), while XDR-TB included MDR/RR-TB with resistance to any FLQ and at least one additional group A drug. Mutation status was determined by comparing bands on reaction zones [gyrA and gyrB for FLQ resistance, rrs for SILD resistance, and eis for low-level kanamycin resistance, according to the GenoType MTBDRsl VER 2.0, Hain Lifescience GmbH, Nehren, Germany definition of pre-XDR and XDR] to the evaluation sheet. SPSS version 17.0 was used for data analysis.
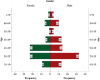
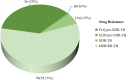
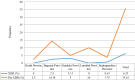
Results: Out of a total of 171 patients with MDR/RR-TB, 160 had (93.57%) had MTBC, of whom 57 (35.63%) had pre-XDR-TB and 10 (6.25%) had XDR-TB. Among the pre-XDR-TB strains, 56 (98.25%) were FLQ resistant, while 1 (1.75%) was SLID resistant. The most frequent mutations were found at codons MUT3C (57.14%, 32/56) and MUT1 (23.21%, 13/56) of the gyrA gene. One patient had SLID resistant genotype at the MUT1 codon of the rrs gene (100%, 1/1). XDR-TB mutation bands were mostly detected on MUT1 (30%, 3/10) of the gyrA and rrs, MUT3C (30%, 3/10) of the gyrA, and MUT1 (30%, 3/10) of the rrs.
Conclusions: Pre-XDR-TB had a significantly higher likelihood than XDR-TB, with different specific mutation bands present in gyrA and rrs genes.
Copyright: © 2024 Chand et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk assessment and transmission of fluoroquinolone resistance in drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis: a retrospective genomic epidemiology study.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 24;14(1):19719. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70535-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39181942 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic analysis of drug-resistant tuberculosis in Ghana: Insights into pre-XDR and XDR-TB.PLoS One. 2025 May 20;20(5):e0323527. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323527. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40392805 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of mutations associated with resistance to second-line tuberculosis drug among multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients from high prevalence tuberculosis city in Morocco.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Feb 27;18(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3009-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29486710 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance acquisition versus primary transmission in the presentation of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2022 Oct-Dec;11(4):343-348. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_187_22. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2022. PMID: 36510916 Review.
-
Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: new strains, new challenges.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008 Oct;6(5):713-24. doi: 10.1586/14787210.6.5.713. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008. PMID: 18847407 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Tuberculosis. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis (accessed on 28/03/2021).
-
- Marini RP, Wachtman LM, Tardif SD, Mansfield K, Fox JG, editors. The common marmoset in captivity and biomedical research. Academic Press; 2018. Nov 19.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.Tuberculosis (TB); How TB Spreads. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/basics/howtbspreads.htm (accessed on 28/03/2021).
-
- World Health Organization, South-East Asia; Tuberculosis. Tuberculosis in South-East Asia Region. Available at: https://www.who.int/southeastasia/health-topics/tuberculosis (accessed on 28/03/2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

