Commercial human 3D corneal epithelial equivalents for modeling epithelial infection in herpes keratitis
- PMID: 38710129
- PMCID: PMC12107712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2024.110096
Commercial human 3D corneal epithelial equivalents for modeling epithelial infection in herpes keratitis
Abstract
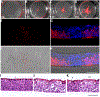
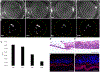
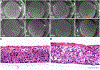
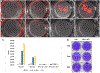
Herpes stromal keratitis is the leading cause of infectious blindness in the western world. Infection by HSV1 is most common, but VZV and hCMV also infect the cornea. Multiple models of HSV1 corneal infection exist, but none for VZV and hCMV because of their host specificity. Here, we used commercially available 3D human corneal epithelial equivalents (HCEE) to study infection by these herpesviruses. HCEE was infected by HSV-1 and hCMV without requiring scarification and resulted in spreading infections. Spread of HSV-1 infection was rapid, while that of hCMV was slow. In contrast, infections with VZV required damage to the HCEE and did not spread. Acyclovir dramatically reduced replication of HSV-1 in this model. We conclude that highly quality-controlled, readily available HCEE is a useful model to study human-restricted herpesvirus infection of the human corneal epithelium and for screening of antiviral drugs for treating HSK in an 3D model system.
Keywords: 3D culture; Drug testing; Herpes keratitis; Herpes zoster ophthalmicus; Herpesvirus.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Alépée N, Adriaens E, Abo T, Bagley D, Desprez B, Hibatallah J, Mewes K, Pfannenbecker U, Sala À, Van Rompay AR, Verstraelen S, McNamee P, 2019. Development of a defined approach for eye irritation or serious eye damage for neat liquids based on cosmetics Europe analysis of in vitro RhCE and BCOP test methods. Toxicol. Vitro 59, 100–114. 10.1016/j.tiv.2019.04.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Avivi C, Goldstein RS, 1999. Differential expression of Islet-1 in neural crest derived ganglia: islet-1+ dorsal root ganglion cells are post-mitotic and Islet-1+ sympathetic ganglion cells are still cycling. Dev. Brain Res 115, 89–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

