Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) inhibitor camonsertib dose optimization in patients with biomarker-selected advanced solid tumors (TRESR study)
- PMID: 38710487
- PMCID: PMC11378309
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djae098
Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) inhibitor camonsertib dose optimization in patients with biomarker-selected advanced solid tumors (TRESR study)
Abstract
Background: Camonsertib is a selective oral inhibitor of ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) kinase with demonstrated efficacy in tumors with DNA damage response gene deficiencies. On-target anemia is the main drug-related toxicity typically manifesting after the period of dose-limiting toxicity evaluation. Thus, dose and schedule optimization requires extended follow-up to assess prolonged treatment effects.
Methods: Long-term safety, tolerability, and antitumor efficacy of 3 camonsertib monotherapy dosing regimens were assessed in the TRESR study dose-optimization phase: 160 mg once daily (QD) 3 days on, 4 days off (160 3/4; the preliminary recommended Phase II dose [RP2D]) and two step-down groups of 120 mg QD 3/4 (120 3/4) and 160 mg QD 3/4, 2 weeks on, 1 week off (160 3/4, 2/1w). Safety endpoints included incidence of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), dose modifications, and transfusions. Efficacy endpoints included overall response rate, clinical benefit rate, progression-free survival, and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)-based molecular response rate.
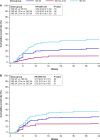
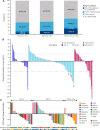
Results: The analysis included 119 patients: 160 3/4 (n = 67), 120 3/4 (n = 25), and 160 3/4, 2/1w (n = 27) treated up to 117.1 weeks as of the data cutoff. The risk of developing grade 3 anemia was significantly lower in the 160 3/4, 2/1w group compared with the preliminary RP2D group (hazard ratio = 0.23, 2-sided P = .02), translating to reduced transfusion and dose reduction requirements. The intermittent weekly schedule did not compromise antitumor activity.
Conclusion: The 160 3/4, 2/1w dose was established as an optimized regimen for future camonsertib monotherapy studies offering a substantial reduction in the incidence of anemia without any compromise to efficacy.
Clinical trial id: NCT04497116.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Elisa Fontana has received personal funding for conference attendance from Repare Therapeutics, CARIS Life Science, Seagen, Sapience Pharma, and BicycleTx Ltd; and has received research funding paid to their institution by Acerta Pharma, ADC Therapeutics, Amgen, Arcus Biosciences, Array BioPharma, Artios Pharma Ltd, Astellas Pharma, Inc., Astex, AstraZeneca, Basilea, Bayer, BeiGene, BicycleTx Ltd, BioNTech, Blueprint Medicines, Boehringer Ingelheim, Calithera Biosciences, Inc., Carrick Therapeutics, Casi Pharmaceuticals, Clovis Oncology, Inc., Crescendo Biologics Ltd, CytomX Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, Deciphera, Eli Lilly, Ellipses, Exelixis, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Fore Biotherapeutics, G1 Therapeutics, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, H3 Biomedicine, Inc., Hutchinson MediPharma, Ignyta/Roche, Immunocore, Immunomedics, Inc., Incyte, Instil Bio, IOVANCE, Janssen, Jiangsu Hengrui, Kronos Bio, Lupin Limited, MacroGenics, Menarini, Merck KGaA, Mereo BioPharma, Merus, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Nerviano Medical Sciences, Nurix Therapeautics, Inc., Oncologie, Oxford Vacmedix, Pfizer, Plexxikon Inc., QED Therapeutics, Inc., Relay Therapeutics, Repare Therapeutics, Ribon Therapeutics, Roche, Sapience, Seagen, Servier, Stemline, Synthon Biopharmaceuticals, Taiho, Tesaro, Turning Point Therapeutics, Inc.
Ezra Rosen is a study investigator.
Elizabeth K. Lee has received research funding from Merck and consulting funding from Aadi Biosciences.
Martin Højgaard has received research funding or contracts paid to their institution by Repare Therapeutics, Puma Biotechnology, AstraZeneca, Incyte Corporation, Pfizer, Orion Pharma, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novarits, Eli Lilly Pharmaceuticals/Loxo Oncology, Bayer, Amgen, Genmab, Kinnate Biopharma, Bioinvent, Dragonfly Therapeutics, and Roche/Genentech.
Niharika B. Mettu has received research funding paid to their institution by Incyte Corporation, Genentech/Roche, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Erytech Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Amphivena Therapeutics, Repare Therapeutics, BioMed Valley Discoveries, Mereo Biopharma, Syros, Aravive, and Merck.
Stephanie Lheureux has received grants or contracts paid to their institution from Merck, AstraZeneca, Regeneron, Roche, Repare Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline, and Seagen; consulting fees from Novocure, Merck, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Eisai, and Shattuck Labs; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, and Eisai/Merck; and participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board from AstraZeneca.
Benedito A. Carneiro has received research funding paid to their institution by AstraZeneca, Abbvie, Actuate Therapeutics, Astellas, Bayer, Dragonfly Therapeutics, Pfizer, and Repare Therapeutics.
Gregory M. Cote has received funding paid to their institution by Servier Pharmaceuticals, Epizyme, PharmaMar, Macrogenics, Eisai, Merck KGaA/EMD Serono Research and Development Institute, Bavarian-Nordic, Bayer, SpringWorks, Repare Therapeutics, Foghorn, SMP Oncology, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, RAIN Therapeutics, BioAtla, lnhibrx, lkena, and C4 Therapeutics; and advisory board fees from Epizyme, PharmaMar, Eisai, Foghorn, lkena, and C4 Therapeutics.
Louise Carter is a study investigator; and has performed consultancy work for Boehringer Ingelheim, Bicycle Therapeutics, and Athenex.
Ruth Plummer has received honoraria for attending advisory boards from Pierre Faber, Bayer, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ellipses, Immunocore, Genmab, Astex Therapeutics, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Nerviano, AmLo, Incyte, Cybrexa Benevolent AI, and Sanofi; honoraria for working as an independent data monitoring committee member for Alligator Biosciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Onxeo, SOTIO Biotech AG, and AstraZeneca; personal funding for delivery of educational talks or chairing educational meetings by AstraZeneca, Novartis, Bayer, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Bristol Myers Squibb; and funds to support attendance at conferences from Merck Sharp & Dohme and Bristol Myers Squibb.
Devalingam Mahalingam has received research funding from Merck, Oncolytics, and Amgen; scientific advisory board for Qurient and OncoOne; and an advisory/speaker bureau for Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, and Exelixis.
Adrian J. Fretland, Joseph D. Schonhoft, Ian M. Silverman, Marisa Wainszelbaum, Danielle Ulanet, and Maria Koehler are employees of Repare Therapeutics and may hold stock and/or stock options.
Timothy A. Yap is an employee of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, where he is Vice President, Head of Clinical Development in the Therapeutics Discovery Division, which has a commercial interest in DNA damage response and other inhibitors (IACS30380/ART0380 was licensed to Artios); has received funding paid to their institution from Acrivon, Artios, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Beigene, BioNTech, Blueprint, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boundless Bio, Clovis, Constellation, Cyteir, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Forbius, F-Star, GlaxoSmithKline, Genentech, Haihe, Ideaya ImmuneSensor, Insilico Medicine, Ionis, Ipsen, Jounce, Karyopharm, KSQ Therapeutics, Kyowa, Merck, Mirati, Novartis, Pfizer, Ribon Therapeutics, Regeneron, Repare, Rubius, Sanofi, Scholar Rock, Seattle Genetics, Tango, Tesaro, Vivace, and Zenith; has received consultancy funding from AbbVie, Acrivon, Adagene, Almac, Aduro, Amphista, Artios, Astex, AstraZeneca, Athena, Atrin, Avenzo, Avoro, Axiom, Baptist Health Systems, Bayer, Beigene, BioCity Pharma, Blueprint, Boxer, Bristol Myers Squibb, C4 Therapeutics, Calithera, Cancer Research UK, Carrick Therapeutics, Circle Pharma, Clovis, Cybrexa, Daiichi Sankyo, Dark Blue Therapeutics, Diffusion, Duke Street Bio, 858 Therapeutics, EcoR1 Capital, Ellipses Pharma, EMD Serono, Entos, F-Star, Genesis Therapeutics, Genmab, Glenmark, GLG Pharma, Globe Life Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Guidepoint, Ideaya Biosciences, Idience, Ignyta, I-Mab, ImmuneSensor, Impact Therapeutics, Institut Gustave Roussy, Intellisphere, Jansen, Kyn, MEI Pharma, Mereo, Merck, Merit, Monte Rosa Therapeutics, Natera, Nested Therapeutics, Nexys, Nimbus, Novocure, Odyssey, OHSU, OncoSec, Ono Pharma, Onxeo, PanAngium Therapeutics, Pegascy, PER, Pfizer, Piper-Sandler, Pliant Therapeutics, Prolynx, Radiopharma Theranostics, Repare, resTORbio, Roche, Ryvu Therapeutics, SAKK, Sanofi, Schrodinger, Servier, Synnovation, Synthis Therapeutics, Tango, TCG Crossover, TD2 Translational Drug Development, Terremoto Biosciences, Tessellate Bio, Theragnostics, Terns Pharmaceuticals, Tolremo, Tome, Thryv Therapeutics, Trevarx Biomedical, Varian, Veeva, Versant, Vibliome, Voronoi Inc, Xinthera, Zai Labs, and ZielBio; and is a stockholder in Seagen. He was supported by the National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support Grant CA016672 to The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, DOD grants W81XWH2210504_BC211174 and W81XWH-21-1-0282_OC200482, V Foundation Scholar Grant VC2020-001, and NIH R01 grant 1R01CA255074.
Figures

References
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Optimizing the Dosage of Human Prescription Drugs and Biological Products for the Treatment of Oncologic Diseases. Draft Guidance for Industry. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents.... Accessed March 10, 2024.
-
- Wengner AM, Siemeister G, Lücking U, et al. The novel ATR inhibitor BAY 1895344 is efficacious as monotherapy and combined with DNA damage-inducing or repair-compromising therapies in preclinical cancer models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020;19(1):26-38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

