White matter integrity of right frontostriatal circuit predicts internet addiction severity among internet gamers
- PMID: 38711213
- PMCID: PMC11074389
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.13399
White matter integrity of right frontostriatal circuit predicts internet addiction severity among internet gamers
Abstract
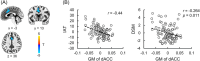
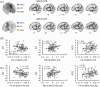
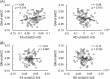
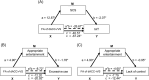
Excessive use of the internet, which is a typical scenario of self-control failure, could lead to potential consequences such as anxiety, depression, and diminished academic performance. However, the underlying neuropsychological mechanisms remain poorly understood. This study aims to investigate the structural basis of self-control and internet addiction. In a cohort of 96 internet gamers, we examined the relationships among grey matter volume and white matter integrity within the frontostriatal circuits and internet addiction severity, as well as self-control measures. The results showed a significant and negative correlation between dACC grey matter volume and internet addiction severity (p < 0.001), but not with self-control. Subsequent tractography from the dACC to the bilateral ventral striatum (VS) was conducted. The fractional anisotropy (FA) and radial diffusivity of dACC-right VS pathway was negatively (p = 0.011) and positively (p = 0.020) correlated with internet addiction severity, respectively, and the FA was also positively correlated with self-control (p = 0.036). These associations were not observed for the dACC-left VS pathway. Further mediation analysis demonstrated a significant complete mediation effect of self-control on the relationship between FA of the dACC-right VS pathway and internet addiction severity. Our findings suggest that the dACC-right VS pathway is a critical neural substrate for both internet addiction and self-control. Deficits in this pathway may lead to impaired self-regulation over internet usage, exacerbating the severity of internet addiction.
Keywords: DTI; VBM; dorsal anterior cingulate cortex; internet addiction; prefrontal‐striatum circuits; self‐control.
© 2024 The Authors. Addiction Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Young KS. Internet addiction: the emergence of a new clinical disorder. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2009;1:237.
-
- Servidio R. Exploring the effects of demographic factors, internet usage and personality traits on Internet addiction in a sample of Italian university students. Comput Hum Behav. 2014;35:85‐92. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2014.02.024 - DOI
-
- Rumpf H‐J, Achab S, Billieux J, et al. Including gaming disorder in the ICD‐11: the need to do so from a clinical and public health perspective: commentary on: a weak scientific basis for gaming disorder: let us err on the side of caution (van Rooij et al., 2018). J Behav Addict. 2018;7(3):556‐561. doi:10.1556/2006.7.2018.59 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 81971245/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 62077042/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021ZD0200409/STI 2030-Major Projects
- MOE Frontiers Science Center for Brain Science & Brain-Machine Integration, Zhejiang University
- Zhejiang Province "Qianjiang Talent Program," Research of Basic Discipline for the 2.0 Base of Top-notch Students Training Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

