Beaconet: A Reference-Free Method for Integrating Multiple Batches of Single-Cell Transcriptomic Data in Original Molecular Space
- PMID: 38711214
- PMCID: PMC11234410
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202306770
Beaconet: A Reference-Free Method for Integrating Multiple Batches of Single-Cell Transcriptomic Data in Original Molecular Space
Abstract
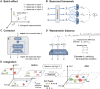
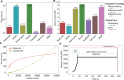
Integrating multiple single-cell datasets is essential for the comprehensive understanding of cell heterogeneity. Batch effect is the undesired systematic variations among technologies or experimental laboratories that distort biological signals and hinder the integration of single-cell datasets. However, existing methods typically rely on a selected dataset as a reference, leading to inconsistent integration performance using different references, or embed cells into uninterpretable low-dimensional feature space. To overcome these limitations, a reference-free method, Beaconet, for integrating multiple single-cell transcriptomic datasets in original molecular space by aligning the global distribution of each batch using an adversarial correction network is presented. Through extensive comparisons with 13 state-of-the-art methods, it is demonstrated that Beaconet can effectively remove batch effect while preserving biological variations and is superior to existing unsupervised methods using all possible references in overall performance. Furthermore, Beaconet performs integration in the original molecular feature space, enabling the characterization of cell types and downstream differential expression analysis directly using integrated data with gene-expression features. Additionally, when applying to large-scale atlas data integration, Beaconet shows notable advantages in both time- and space-efficiencies. In summary, Beaconet serves as an effective and efficient batch effect removal tool that can facilitate the integration of single-cell datasets in a reference-free and molecular feature-preserved mode.
Keywords: batch effects; large‐scale; molecular feature space; reference‐free; single‐cell datasets.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
SCITUNA: single-cell data integration tool using network alignment.BMC Bioinformatics. 2025 Mar 27;26(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06087-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40148808 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Multiple Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Datasets Using Adversarial Autoencoders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 13;24(6):5502. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065502. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982574 Free PMC article.
-
iSMNN: batch effect correction for single-cell RNA-seq data via iterative supervised mutual nearest neighbor refinement.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Sep 2;22(5):bbab122. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab122. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33839756 Free PMC article.
-
Feature selection revisited in the single-cell era.Genome Biol. 2021 Dec 1;22(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02544-3. Genome Biol. 2021. PMID: 34847932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selecting gene features for unsupervised analysis of single-cell gene expression data.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Nov 5;22(6):bbab295. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab295. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 34351383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RGCN-BA: relational graph convolutional network with batch awareness for single-cell RNA sequencing clustering.Brief Bioinform. 2025 Jul 2;26(4):bbaf378. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf378. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40728858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rozenblatt‐Rosen O., Stubbington M. J. T., Regev A., Teichmann S. A., Nature 2017, 550, 451. - PubMed
-
- Han X., Wang R., Zhou Y., Fei L., Sun H., Lai S., Saadatpour A., Zhou Z., Chen H., Ye F., Huang D., Xu Y., Huang W., Jiang M., Jiang X., Mao J., Chen Y., Lu C., Xie J., Fang Q., Wang Y., Yue R., Li T., Huang H., Orkin S. H., Yuan G.‐C., Chen M., Guo G., Cell 2018, 172, 1091. - PubMed
-
- Zhang F., Wei K., Slowikowski K., Fonseka C. Y., Rao D. A., Kelly S., Goodman S. M., Tabechian D., Hughes L. B., Salomon‐Escoto K., Watts G. F. M., Jonsson A. H., Rangel‐Moreno J., Meednu N., Rozo C., Apruzzese W., Eisenhaure T. M., Lieb D. J., Boyle D. L., Mandelin A. M., Albrecht J., Bridges S. L., Buckley C. D., Buckner J. H., Dolan J., Guthridge J. M., Gutierrez‐Arcelus M., Ivashkiv L. B., James E. A., James J. A., et al., Nature Immunol. 2019, 20, 928. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arazi A., Rao D. A., Berthier C. C., Davidson A., Liu Y., Hoover P. J., Chicoine A., Eisenhaure T. M., Jonsson A. H., Li S., Lieb D. J., Zhang F., Slowikowski K., Browne E. P., Noma A., Sutherby D., Steelman S., Smilek D. E., Tosta P., Apruzzese W., Massarotti E., Dall'Era M., Park M., Kamen D. L., Furie R. A., Payan‐Schober F., Pendergraft W. F., McInnis E. A., Buyon J. P., Petri M. A., et al., Nature Immunol. 2019, 20, 902. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
