Identification of Dof transcription factors in Dendrobium huoshanense and expression pattern under abiotic stresses
- PMID: 38711915
- PMCID: PMC11070552
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1394790
Identification of Dof transcription factors in Dendrobium huoshanense and expression pattern under abiotic stresses
Abstract
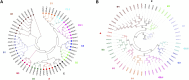
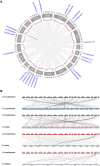
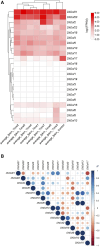
Introduction: DNA-binding with one finger (Dof) transcription factors (TFs) are a unique family of TFs found in higher plants that regulate plant responses to light, hormones, and abiotic stresses. The specific involvement of Dof genes in the response to environmental stresses remains unknown in D. huoshanense. Methods: A total of 22 Dof family genes were identified from the D. huoshanense genome. Results: Chromosome location analysis showed that DhDof genes were distributed on 12 chromosomes, with the largest number of Dof genes located on chromosome 8. The phylogenetic tree revealed that DhDofs could be categorized into 11 distinct subgroups. In addition to the common groups, DhDof4, DhDof5, DhDof17, and the AtDof1.4 ortholog were clustered into the B3 subgroup. Group E was a newly identified branch, among which DhDof6, DhDof7, DhDof8, and DhDof9 were in an independent branch. The conserved motifs and gene structure revealed the differences in motif number and composition of DhDofs. The dof domain near the N-terminus was highly conserved and contained a C2-C2-type zinc finger structure linked with four cysteines. Microsynteny and interspecies collinearity revealed gene duplication events and phylogenetic tree among DhDofs. Large-scale gene duplication had not occurred among the DhDofs genes and only in one pair of genes on chromosome 13. Synteny blocks were found more often between D. huoshanense and its relatives and less often between Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana. Selection pressure analysis indicated that DhDof genes were subject to purifying selection. Expression profiles and correlation analyses revealed that the Dof gene under hormone treatments showed several different expression patterns. DhDof20 and DhDof21 had the highest expression levels and were co-expressed under MeJA induction. The cis-acting element analysis revealed that each DhDof had several regulatory elements involved in plant growth as well as abiotic stresses. qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated that DhDof2 was the main ABA-responsive gene and DhDof7 was the main cold stress-related gene. IAA suppressed the expression of some Dof candidates, and SA inhibited most of the candidate genes. Discussion: Our results may provide new insights for the further investigation of the Dof genes and the screening of the core stress-resistance genes.
Keywords: DNA binding with one finger; Dendrobium huoshanense; abiotic stress; bioinformactics analysis; phylogeny.
Copyright © 2024 Gu, Zhang, Wang, He, Chen, Zhang and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Plant AT-rich protein and zinc-binding protein (PLATZ) family in Dendrobium huoshanense: identification, evolution and expression analysis.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Dec 30;24(1):1276. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-06009-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39736596 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Insight and Expression Pattern of WUSCHEL-Related Homebox Genes of Dendrobium huoshanense.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Feb 23;13(3):e70057. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70057. eCollection 2025 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40008241 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Characterization of the Dof Family in Dendrobium officinale.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 16;26(6):2671. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062671. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141313 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of Dof family transcription factors and their responses to abiotic stresses in Chinese cabbage.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jan 31;16(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1242-9. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25636232 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the Dof gene family reveals their involvement in hormone response and abiotic stresses in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.).Gene. 2024 Jun 5;910:148336. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148336. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Gene. 2024. PMID: 38447680 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Based Identification of the Dof Gene Family in Three Cymbidium Species and Their Responses to Heat Stress in Cymbidium goeringii.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 12;25(14):7662. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147662. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062906 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide identification of Dof transcription factors in Carmine radish reveals RsDof33 role in cadmium stress and anthocyanin biosynthesis.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 8;15(1):4766. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88308-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39922841 Free PMC article.
-
Plant AT-rich protein and zinc-binding protein (PLATZ) family in Dendrobium huoshanense: identification, evolution and expression analysis.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Dec 30;24(1):1276. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-06009-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39736596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corrales A. R., Nebauer S. G., Carrillo L., Fernández-Nohales P., Marqués J., Renau-Morata B., et al. (2014). Characterization of tomato Cycling Dof Factors reveals conserved and new functions in the control of flowering time and abiotic stress responses. J. Exp. Bot. 65, 995–1012. 10.1093/jxb/ert451 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fornara F., Panigrahi K. C. S., Gissot L., Sauerbrunn N., Rühl M., Jarillo J. A., et al. (2009). Arabidopsis DOF transcription factors act redundantly to reduce CONSTANS expression and are essential for a photoperiodic flowering response. Dev. Cell 17, 75–86. 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.015 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

