Diagnostic value of retinol-binding protein 4 in diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38711978
- PMCID: PMC11070506
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1356131
Diagnostic value of retinol-binding protein 4 in diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a major microvascular complication of diabetes and the leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Early detection and prevention of DN are important. Retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) has been considered as a single diagnostic marker for the detection of renal impairment. However, the results have been inconsistent. The present meta-analysis aimed to determine the diagnostic potential of RBP4 in patients in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with DN.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Wanfang and CNKI databases from inception until January 2024. The meta-analysis was performed by Stata version 15.0, and sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios (PLR and NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) and area under the curve (AUC) were pooled. The Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 tool was utilized to assess the quality of each included study. In addition, heterogeneity and publication bias were evaluated.
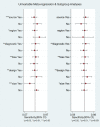
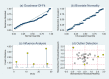
Results: Twenty-nine studies were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.76 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.71-0.80] and 0.81 (95% CI, 0.76-0.85), respectively. The results showed a pooled PLR of 4.06 (95% CI, 3.16-5.21), NLR of 0.29 (95% CI, 0.24-0.36) and DOR of 13.76 (95% CI, 9.29-20.37). The area under the summarized receiver operating characteristic curve was given a value of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.82-0.88). No obvious publication bias existed in the Deeks' funnel plot asymmetry test.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that RBP4 has a promising diagnostic value with good sensitivity and specificity for patients with T2DM with DN.
Keywords: biomarkers; diabetic nephropathy; diagnosis; meta-analysis; retinol-binding protein 4.
Copyright © 2024 Cao, Zhong, Jin, Hu, Wang, Shi and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

