Longitudinal study of immunity to SARS-CoV2 in ocrelizumab-treated MS patients up to 2 years after COVID-19 vaccination
- PMID: 38713096
- PMCID: PMC11251481
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.52081
Longitudinal study of immunity to SARS-CoV2 in ocrelizumab-treated MS patients up to 2 years after COVID-19 vaccination
Abstract
Objectives: (1) To plot the trajectory of humoral and cellular immune responses to the primary (two-dose) COVID-19 mRNA series and the third/booster dose in B-cell-depleted multiple sclerosis (MS) patients up to 2 years post-vaccination; (2) to identify predictors of immune responses to vaccination; and (3) to assess the impact of intercurrent COVID-19 infections on SARS CoV-2-specific immunity.
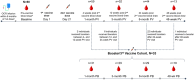
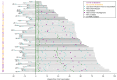
Methods: Sixty ocrelizumab-treated MS patients were enrolled from NYU (New York) and University of Colorado (Anschutz) MS Centers. Samples were collected pre-vaccination, and then 4, 12, 24, and 48 weeks post-primary series, and 4, 12, 24, and 48 weeks post-booster. Binding anti-Spike antibody responses were assessed with multiplex bead-based immunoassay (MBI) and electrochemiluminescence (Elecsys®, Roche Diagnostics), and neutralizing antibody responses with live-virus immunofluorescence-based microneutralization assay. Spike-specific cellular responses were assessed with IFNγ/IL-2 ELISpot (Invitrogen) and, in a subset, by sequencing complementarity determining regions (CDR)-3 within T-cell receptors (Adaptive Biotechnologies). A linear mixed-effect model was used to compare antibody and cytokine levels across time points. Multivariate analyses identified predictors of immune responses.
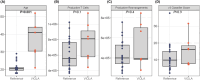
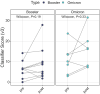
Results: The primary vaccination induced an 11- to 208-fold increase in binding and neutralizing antibody levels and a 3- to 4-fold increase in IFNγ/IL-2 responses, followed by a modest decline in antibody but not cytokine responses. Booster dose induced a further 3- to 5-fold increase in binding antibodies and 4- to 5-fold increase in IFNγ/IL-2, which were maintained for up to 1 year. Infections had a variable impact on immunity.
Interpretation: Humoral and cellular benefits of COVID-19 vaccination in B-cell-depleted MS patients were sustained for up to 2 years when booster doses were administered.
© 2024 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by an unrestricted investigator‐initiated grant from Genentech.
Figures

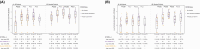

Similar articles
-
Humoral and T-Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis Treated With Ocrelizumab.JAMA Neurol. 2021 Dec 1;78(12):1510-1514. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.3599. JAMA Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34554197 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal cellular and humoral immune responses following COVID-19 BNT162b2-mRNA-based booster vaccination of craft and manual workers in Qatar.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 27;16:1557426. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557426. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40213554 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral and cellular immune response from first to fourth SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in anti-CD20-treated multiple sclerosis patients-a longitudinal cohort study.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 5;15:1432348. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1432348. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39301017 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine challenges in CLL: a comprehensive exploration of efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 immunization for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Ann Hematol. 2024 Dec;103(12):4971-4980. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05869-8. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39008060
-
Examining the immunological responses to COVID-19 vaccination in multiple myeloma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Geriatr. 2024 May 8;24(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05006-0. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38720296 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recall vaccination increases detectable B-cell reactivity in persons with multiple sclerosis treated with ocrelizumab.J Neurol. 2025 Apr 4;272(4):314. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13027-x. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40186086
-
Vaccine-Induced Humoral and Cellular Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Multiple Sclerosis Patients on Ocrelizumab.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Apr 30;13(5):488. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13050488. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40432100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schiavetti I, Cordioli C, Stromillo ML, et al. Breakthrough SARS‐CoV‐2 infections in MS patients on disease‐modifying therapies. Mult Scler. 2022;28(13):2106‐2111. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
