Global Burden and Trends of Primary Liver Cancer Attributable to Comorbid Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among People Living with Hepatitis B: An Observational Trend Study from 1990 to 2019
- PMID: 38713342
- PMCID: PMC11176116
- DOI: 10.1007/s44197-024-00237-1
Global Burden and Trends of Primary Liver Cancer Attributable to Comorbid Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among People Living with Hepatitis B: An Observational Trend Study from 1990 to 2019
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) increases the risk of liver cancer among people living with hepatitis B virus (HBV). Our study aimed to estimate the global burden and trends of liver cancer attributable to comorbid T2DM among people living with HBV from 1990 to 2019.
Methods: We calculated the population attributable fractions (PAFs) of liver cancer attributable to comorbid T2DM among the burden of HBV-related liver cancer. We applied the PAFs to the burden of HBV-related liver cancer derived from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2019 database to obtain the burden of liver cancer attributable to HBV-T2DM comorbidity. The prevalence, disability-adjusted life year (DALY), and deaths of liver cancer attributable to the comorbidity were assessed at the global, regional, and country levels and then stratified by the sociodemographic index (SDI), sex, and age group. Estimated annual percentage changes (EAPCs) were calculated to quantify the temporal trends.
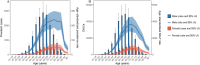
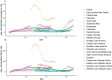
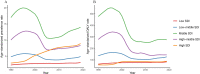
Results: In 2019, the global age-standardized prevalence and DALY rates of liver cancer attributable to HBV-T2DM comorbidity were 9.9 (8.4-11.5) and 182.4 (154.9-212.7) per 10,000,000 individuals, respectively. High-income Asia Pacific and East Asia had the highest age-standardized prevalence and DALY rates of liver cancer attributable to HBV-T2DM comorbidity, respectively. From 1990 to 2019, age-standardized prevalence and DALY rates increased in 16 out of 21 GBD regions. High-income North America had the largest annual increases in both age-standardized prevalence rates (EAPC = 6.07; 95% UI, 5.59 to 6.56) and DALY rates (EAPC = 4.77; 95% UI, 4.35 to 5.20), followed by Australasia and Central Asia. Across all SDI regions, the high SDI region exhibited the most rapid increase in age-standardized prevalence and DALY rates from 1990 to 2019. Additionally, men had consistently higher disease burdens than women across all age groups. The patterns of mortality burden and trends are similar to those of DALYs.
Conclusions: The burden of liver cancer attributable to comorbid T2DM among people living with HBV has exhibited an increasing trend across most regions over the last three decades. Tailored prevention strategies targeting T2DM should be implemented among individuals living with HBV.
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus; Disability-adjusted life years; Global Burden of Disease; Hepatitis B virus; Liver neoplasms; Prevalence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Combating hepatitis B and C to reach elimination by 2030. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/combating-hepatitis-b-and-c-to-r.... Accessed 22 Aug 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82204154/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 71774178/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020A1515110230/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2021A1515011765/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2021M693594/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

