An Innovative Treatment Using Calcium Hydroxyapatite for Non-Surgical Facial Rejuvenation: The Vectorial-Lift Technique
- PMID: 38714538
- PMCID: PMC11499372
- DOI: 10.1007/s00266-024-04071-5
An Innovative Treatment Using Calcium Hydroxyapatite for Non-Surgical Facial Rejuvenation: The Vectorial-Lift Technique
Erratum in
-
Correction: An Innovative Treatment Using Calcium Hydroxyapatite for Non-Surgical Facial Rejuvenation: The Vectorial-Lift Technique.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Aug;48(15):3058. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04167-y. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38869520 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
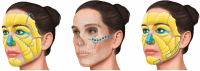
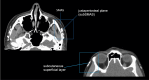
Background: The facial aging process entails alterations in the volume, shape, and texture of all skin layers over time. Calcium hydroxyapatite (CaHA) is a well-established safe skin filler with unique properties to resolve some skin alterations by stimulating neocollagenesis. The vectoral-lift (V-lift) technique targets the global repositioning of facial structures by addressing distinct anatomical injection planes. It includes deep facial augmentation with Radiesse PlusTM to retain ligament restructuring and superficial subcutaneous enhancement with diluted Radiesse DuoTM. Herein, we present cases that illustrate the use of this approach.
Methods: This pilot study enrolled 36 participants (33 women and three men; ages 37-68 years) in a Brazilian clinical setting, and all patients underwent a single treatment. Photographs were taken at rest, in frontal and oblique views, before injection, and 90 days after treatment.
Results: Treatment resulted in elevation of the upper and middle face, notable improvements in the infraorbital hollow, and adjustment of the mean facial volume.
Conclusions: The V-lift technique is a three-dimensional pan-facial treatment that relies on ligament support and face vectoring to obtain a lifting effect and facial contour restoration. It encompasses deep facial augmentation involving the use of Radiesse PlusTM for restructuring and retaining ligaments and Radiesse DuoTM for superficial subcutaneous enhancement. This approach targets a global repositioning of the facial structures by addressing distinct anatomical injection planes. It achieves a repositioning of the overall facial anatomy without requiring a substantial volumetric expansion.
Level of evidence iv: This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266 .
Keywords: Aesthetics; Biostimulation; Calcium hydroxyapatite; Collagen; Dermatology; Plastic surgery; Skin aging.
© 2024. The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
A.R.T. de Almeida has been a consultant to Allergan Inc. and Merz and has participated in clinical trials for Allergan and Galderma. Mariana Muniz is a medical consultant and speaker for Merz Aesthetics. The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, or publication of this article.
Figures








References
-
- Devgan L, Singh P, Durairaj K (2019) Minimally invasive facial cosmetic procedures. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 52:443–459 - PubMed
-
- Mendelson B, Wong CH (2020) Changes in the facial skeleton with aging: implications and clinical applications in facial rejuvenation. Aesthet Plast Surg 44:1151–1158 - PubMed
-
- Emer J, Sundaram H (2013) Aesthetic applications of calcium hydroxylapatite volumizing filler: an evidence-based review and discussion of current concepts: (part 1 of 2). J Drugs Dermatol 12:1345–1354 - PubMed
-
- Mckee D, Remington K, Swift A, Lambros V, Comstock J, Lalonde D (2019) Effective rejuvenation with hyaluronic acid fillers: current advanced concepts. Plast Reconstr Surg 143:1277e–1289e - PubMed
-
- Cong LY, Duan J, Luo CE, Luo SK (2021) Injectable filler technique for face lifting based on dissection of true facial ligaments. Aesthet Surg J 41:NP1571–NP1583 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

