Identification of circRNAs expression profiles and functional networks in parotid gland of type 2 diabetes mouse
- PMID: 38714918
- PMCID: PMC11077881
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10290-6
Identification of circRNAs expression profiles and functional networks in parotid gland of type 2 diabetes mouse
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a novel kind of non-coding RNAs proved to play crucial roles in the development of multiple diabetic complications. However, their expression and function in diabetes mellitus (DM)-impaired salivary glands are unknown.
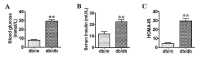
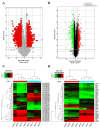
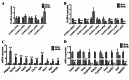
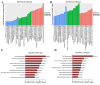
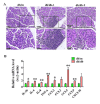
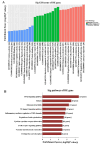
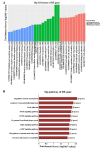
Results: By using microarray technology, 663 upregulated and 999 downregulated circRNAs companied with 813 upregulated and 525 downregulated mRNAs were identified in the parotid glands (PGs) of type2 DM mice under a 2-fold change and P < 0.05 cutoff criteria. Gene ontology (GO) and kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) analysis of upregulated mRNAs showed enrichments in immune system process and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) signaling pathway. Infiltration of inflammatory cells and increased inflammatory cytokines were observed in diabetic PGs. Seven differently expressed circRNAs validated by qRT-PCR were selected for coding-non-coding gene co-expression (CNC) and competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks analysis. PPAR signaling pathway was primarily enriched through analysis of circRNA-mRNA networks. Moreover, the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks highlighted an enrichment in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton.
Conclusion: The inflammatory response is elevated in diabetic PGs. The selected seven distinct circRNAs may attribute to the injury of diabetic PG by modulating inflammatory response through PPAR signaling pathway and actin cytoskeleton in diabetic PGs.
Keywords: Actin cytoskeleton; Circular RNAs; Diabetes mellitus; Inflammation response; Parotid gland.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA and mRNA profile analysis in the parotid gland of mouse with type 2 diabetes.Life Sci. 2021 Mar 1;268:119009. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.119009. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33412210
-
Identification of Serum Exosome-Derived circRNA-miRNA-TF-mRNA Regulatory Network in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Using Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation in Peripheral Blood-Derived Mononuclear Cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 9;13:899503. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.899503. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35757392 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of circRNA Expression Profiles and Analysis of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Networks in an Animal (Mouse) Model of Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Curr Eye Res. 2020 Sep;45(9):1173-1180. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1722179. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Curr Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31979995
-
Comparative analysis of circRNA expression profile and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network between palmitic and stearic acid-induced lipotoxicity to pancreatic β cells.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):9031-9045. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1992333. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34654356 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive circular RNA expression profiling with associated ceRNA network in orbital venous malformation.Mol Vis. 2022 May 20;28:83-95. eCollection 2022. Mol Vis. 2022. PMID: 35814499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenspan D. Xerostomia: diagnosis and management. Oncol (Williston Park) 1996;10(3 Suppl):7–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

