Multi-epitope protein production and its application in the diagnosis of opisthorchiasis
- PMID: 38715089
- PMCID: PMC11077728
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-024-06285-7
Multi-epitope protein production and its application in the diagnosis of opisthorchiasis
Abstract
Background: Opisthorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) continue to be public health concerns in many Southeast Asian countries. Although the prevalence of opisthorchiasis is declining, reported cases tend to have a light-intensity infection. Therefore, early detection by using sensitive methods is necessary. Several sensitive methods have been developed to detect opisthorchiasis. The immunological detection of antigenic proteins has been proposed as a sensitive method for examining opisthorchiasis.
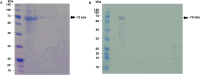
Methods: The Opisthorchis viverrini antigenic proteins, including cathepsin B (OvCB), asparaginyl endopeptidase (OvAEP), and cathepsin F (OvCF), were used to construct multi-antigenic proteins. The protein sequences of OvCB, OvAEP, and OvCF, with a high probability of B cell epitopes, were selected using BepiPred 1.0 and the IEDB Analysis Resource. These protein fragments were combined to form OvCB_OvAEP_OvCF recombinant DNA, which was then used to produce a recombinant protein in Escherichia coli strain BL21(DE3). The potency of the recombinant protein as a diagnostic target for opisthorchiasis was assessed using immunoblotting and compared with that of the gold standard method, the modified formalin-ether concentration technique.
Results: The recombinant OvCB_OvAEP_OvCF protein showed strong reactivity with total immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against light-intensity O. viverrini infections in the endemic areas. Consequently, a high sensitivity (100%) for diagnosing opisthorchiasis was reported. However, cross-reactivity with sera from other helminth and protozoan infections (including taeniasis, strongyloidiasis, giardiasis, E. coli infection, enterobiasis, and mixed infection of Echinostome spp. and Taenia spp.) and no reactivity with sera from patients with non-parasitic infections led to a reduced specificity of 78.4%. In addition, the false negative rate (FNR), false positive rate (FPR), positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and diagnostic accuracy were 0%, 21.6%, 81.4%, 100%, and 88.9%, respectively.
Conclusions: The high sensitivity of the recombinant OvCB_OvAEP_OvCF protein in detecting opisthorchiasis demonstrates its potential as an opisthorchiasis screening target. Nonetheless, research on reducing cross-reactivity should be undertaken by detecting other antibodies in other sample types, such as saliva, urine, and feces.
Keywords: B cell epitopes; Immunoblotting; Multi-antigenic protein; Opisthorchiasis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sayasone S, Utzinger J, Akkhavong K, Odermatt P. Multiparasitism and intensity of helminth infections in relation to symptoms and nutritional status among children: a cross-sectional study in southern Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Acta Trop. 2015;141:322–31. - PubMed
-
- Miyamoto K, Kirinoki M, Matsuda H, Hayashi N, Chigusa Y, Sinuon M, et al. Field survey focused on Opisthorchis viverrini infection in five provinces of Cambodia. Parasitol Int. 2014;63:366–73. - PubMed
-
- Jamornthanyawat N. The diagnosis of human opisthorchiasis. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2002;33:86–91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

