MR spectroscopy in breast cancer metabolomics
- PMID: 38715862
- PMCID: PMC10989566
- DOI: 10.1002/ansa.202000160
MR spectroscopy in breast cancer metabolomics
Abstract
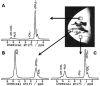
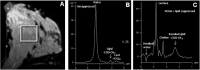
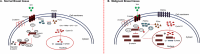
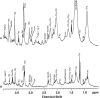
Breast cancer poses a significant health care challenge worldwide requiring early detection and effective treatment strategies for better patient outcome. A deeper understanding of the breast cancer biology and metabolism may help developing better diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Metabolomic studies give a comprehensive analysis of small molecule metabolites present in human tissues in vivo. The changes in the level of these metabolites provide information on the complex mechanism of the development of the disease and its progression. Metabolomic approach using analytical techniques such as magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) has evolved as an important tool for identifying clinically relevant metabolic biomarkers. The metabolic characterization of breast lesions using in-vivo MRS has shown that malignant breast tissues contain elevated levels of choline containing compounds (tCho), suggesting rapid proliferation of cancer cells and alterations in membrane metabolism. Also, tCho has been identified as one of the important biomarkers that help to enhance the diagnostic accuracy of dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and also for monitoring treatment response. Further, metabolome of malignant tissues can be studied using ex vivo and in vitro MRS at high magnetic fields. This provided the advantage of detection of a large number of compounds that facilitated more comprehensive insight into the altered metabolic pathways associated with the cancer development and progression and also in identification of several metabolites as potential biomarkers. This article briefly reviews the role of MRS based metabolic profiling in the discovery of biomarkers and understanding of the altered metabolism in breast cancer.
Keywords: biomarker; breast cancer; ex vivo; in vitro; in vivo; in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS); metabolomics; therapeutic response.
© 2021 The Authors. Analytical Science Advances published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57(1):43‐66. - PubMed
-
- Houssami N, Irwig L, Loy C. Accuracy of combined breast imaging in young women. Breast. 2002;11(1):36‐40. - PubMed
-
- Turnbull LW. Dynamic contrast‐enhanced MRI in the diagnosis and management of breast cancer. NMR Biomed. 2009;22(1):28‐39. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
