A Fast-Growing Myxoma of the Left Atrium
- PMID: 38715873
- PMCID: PMC11073595
- DOI: 10.12890/2024_004490
A Fast-Growing Myxoma of the Left Atrium
Abstract
Introduction: Myxoma of the left atrium is a less typical cause of mitral obstruction. If this develops, a flash pulmonary oedema can be the first manifestation.
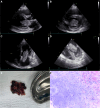
Case description: We present a case report of a 50-year-old woman who was admitted to our internal department because of dyspnoea. The patient overcame a stroke three years before the index hospitalisation with a negative transthoracic echocardiography. By anamnesis and physical examination, an exacerbation of COPD was assumed, and the patient was treated accordingly. As the patient showed numerous risk factors for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, transthoracic echocardiography was performed. A large polypoid mass was found in the left atrium, which caused severe mitral obstruction. Subsequent transoesophageal echocardiography confirmed this finding. The patient underwent urgent cardiac surgery, and the tumour was successfully resected. A histological examination revealed a cardiac myxoma. After the cardiac surgery the patient felt well, and no recurrence of the tumour occurred.
Conclusions: We provide a case report of a fast-growing myxoma that was incidentally found in a patient with dyspnoea. We highlight the fast growth rate of the tumour and the potential for misdiagnosed signs of pulmonary oedema caused by mitral obstruction.
Learning points: Myxomas are the most common primary tumours of the heart, which can manifest a variety of symptoms such as fever, weight loss, thromboembolism, or mitral obstruction.The symptoms of acute exacerbation of COPD and cardiogenic pulmonary oedema can overlap and can be difficult to differentiate by anamnesis and physical examination alone.Transthoracic echocardiography has a high sensitivity for cardiac masses and is the examination of choice when these are suspected.
Keywords: Mitral stenosis; cardiac mass; cardiac surgery; heart tumour; pulmonary oedema.
© EFIM 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Walpot J, Shivalkar B, Rodrigus I, Pasteuning WH, Hokken R. Atrial myxomas grow faster than we think. Echocardiography. 2010;27:E128–131. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
