Screening Splice-Switching Antisense Oligonucleotides in Pancreas-Cancer Organoids
- PMID: 38716830
- PMCID: PMC11387002
- DOI: 10.1089/nat.2023.0070
Screening Splice-Switching Antisense Oligonucleotides in Pancreas-Cancer Organoids
Abstract
Aberrant alternative splicing is emerging as a cancer hallmark and a potential therapeutic target. It is the result of dysregulated or mutated splicing factors, or genetic alterations in splicing-regulatory cis-elements. Targeting individual altered splicing events associated with cancer-cell dependencies is a potential therapeutic strategy, but several technical limitations need to be addressed. Patient-derived organoids are a promising platform to recapitulate key aspects of disease states, and to facilitate drug development for precision medicine. Here, we report an efficient antisense-oligonucleotide (ASO) lipofection method to systematically evaluate and screen individual splicing events as therapeutic targets in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma organoids. This optimized delivery method allows fast and efficient screening of ASOs, e.g., those that reverse oncogenic alternative splicing. In combination with advances in chemical modifications of oligonucleotides and ASO-delivery strategies, this method has the potential to accelerate the discovery of antitumor ASO drugs that target pathological alternative splicing.
Keywords: alternative splicing; antisense oligonucleotide; organoid; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Figures
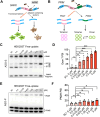
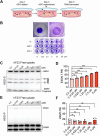
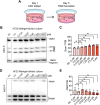
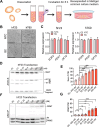
Update of
-
Preclinical Screening of Splice-Switching Antisense Oligonucleotides in PDAC Organoids.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 3:2023.03.31.535161. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.31.535161. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nucleic Acid Ther. 2024 Aug;34(4):188-198. doi: 10.1089/nat.2023.0070. PMID: 37066201 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

