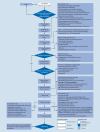
[Treatment algorithm: prone position in critically ill patients]
- PMID: 38717585
- PMCID: PMC11461579
- DOI: 10.1007/s00063-024-01146-8
[Treatment algorithm: prone position in critically ill patients]
Figures
References
-
- Albert RK, Keniston A, Baboi L et al (2014) Prone position-induced improvement in gas exchange does not predict improved survival in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 189:494–496 - PubMed
-
- AWMF (2023) Arbeitsgemeinschaft der Wissenschaftlichen Medizinischen Fachgesellschaften (AWMF). Lagerungstherapie und Mobilisation von kritisch Erkrankten auf Intensivstationen. S3-Leitlinie der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Anästhesiologie und Intensivmedizin e. V. (DGAI). AWMF-Register. NR: 1–15
-
- Bein T, Sabel K, Scherer A et al (2004) Comparison of incomplete (135 degrees ) and complete prone position (180 degrees ) in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Results of a prospective, randomised trial. Anaesthesist 53:1054–1060 - PubMed
-
- Dubb R, Hekler M, Kaltwasser A (2004) Bauchlagerung von Intensivpatienten – Gibt es neue Trends? intensiv 12:4–8
-
- Krüger L, Hauss A, Oldag A et al (2023) Treatment algorithm: oral hygiene in orally intubated patients. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed 118:122–124 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical