Equitable inclusion of diverse populations in oncology clinical trials: deterrents and drivers
- PMID: 38718705
- PMCID: PMC11090874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103373
Equitable inclusion of diverse populations in oncology clinical trials: deterrents and drivers
Abstract
The burden of cancer exerts a disproportionate impact across different regions and population subsets. Disease-specific attributes, coupled with genetic and socioeconomic factors, significantly influence cancer treatment outcomes. Precision oncology promises the development of safe and effective options for specific ethnic phenotypes and clinicodemographic profiles. Currently, clinical trials are concentrated in resource-rich geographies with younger, healthier, white, educated, and empowered populations. Vulnerable and marginalized people are often deprived of opportunities to participate in clinical trials. Despite consistent endeavors by regulators, industry, and other stakeholders, factors including diversity in trial regulations and patient and provider-related cultural, logistic, and operational barriers limit the inclusiveness of clinical trials. Understanding and addressing these constraints by collaborative actions involving regulatory initiatives, industry, patient advocacy groups, community engagement in a culturally sensitive manner, and designing and promoting decentralized clinical trials are vital to establishing a clinical research ecosystem that promotes equity in the representation of population subgroups.
Keywords: clinical trials; diversity; equity; inclusion; regulators.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
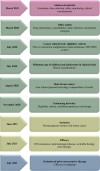
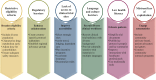
References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

