Magnetic Resonance Imaging Characterization and Clinical Outcomes of Dilated and Arrhythmogenic Left Ventricular Cardiomyopathies
- PMID: 38719365
- PMCID: PMC12042165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2024.02.041
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Characterization and Clinical Outcomes of Dilated and Arrhythmogenic Left Ventricular Cardiomyopathies
Abstract
Background: Nondilated left ventricular cardiomyopathy (NDLVC) has been recently differentiated from dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). A comprehensive characterization of these 2 entities using cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) and genetic testing has never been performed.
Objectives: This study sought to provide a thorough characterization and assess clinical outcomes in a large multicenter cohort of patients with DCM and NDLVC.
Methods: A total of 462 patients with DCM (227) or NDLVC (235) with CMR data from 4 different referral centers were retrospectively analyzed. The study endpoint was a composite of sudden cardiac death or major ventricular arrhythmias.
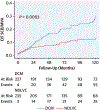
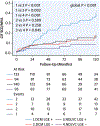
Results: In comparison to DCM, NDLVC had a higher prevalence of pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants of arrhythmogenic genes (40% vs 23%; P < 0.001), higher left ventricular (LV) systolic function (LV ejection fraction: 51% ± 12% vs 36% ± 15%; P < 0.001) and higher prevalence of free-wall late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) (27% vs 14%; P < 0.001). Conversely, DCM showed higher prevalence of pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants of nonarrhythmogenic genes (23% vs 12%; P = 0.002) and septal LGE (45% vs 32%; P = 0.004). Over a median follow-up of 81 months (Q1-Q3: 40-132 months), the study outcome occurred in 98 (21%) patients. LGE with septal location (HR: 1.929; 95% CI: 1.033-3.601; P = 0.039) was independently associated with the risk of sudden cardiac death or major ventricular arrhythmias together with LV dilatation, older age, advanced NYHA functional class, frequent ventricular ectopic activity, and nonsustained ventricular tachycardia.
Conclusions: In a multicenter cohort of patients with DCM and NDLVC, septal LGE together with LV dilatation, age, advanced disease, and frequent and repetitive ventricular arrhythmias were powerful predictors of major arrhythmic events.
Keywords: LGE; SCD; arrhythmias; dilated cardiomyopathy; nondilated left ventricular cardiomyopathy.
Copyright © 2024 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding Support and Author Disclosures This work was supported by the Paul and Ruby Tsai Family Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Career Development Award (Dr Giudicessi); the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute R01HL147064 and R01HL164634 (Drs Mestroni and Taylor). The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Arbelo E, Protonotarios A, Gimeno JR, et al. 2023 ESC guidelines for the management of cardiomyopathies. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(37):3503–3626. - PubMed
-
- Di Marco A, Brown PF, Bradley J, et al. Improved risk stratification for ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(23):2890–2905. - PubMed
-
- Aquaro GD, De Luca A, Cappelletto C, et al. Prognostic value of magnetic resonance phenotype in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(22):2753–2765. - PubMed
-
- Di Marco A, Anguera I, Schmitt M, et al. Late gadolinium enhancement and the risk for ventricular arrhythmias or sudden death in dilated cardiomyopathy: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol HF. 2017;5(1):28–38. - PubMed

