Systematic analysis of NDUFAF6 in complex I assembly and mitochondrial disease
- PMID: 38720117
- PMCID: PMC11395703
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-01039-2
Systematic analysis of NDUFAF6 in complex I assembly and mitochondrial disease
Abstract
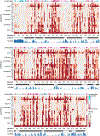
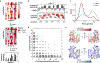
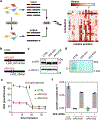
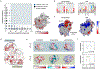
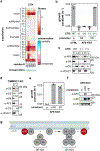
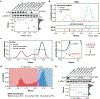
Isolated complex I (CI) deficiencies are a major cause of primary mitochondrial disease. A substantial proportion of CI deficiencies are believed to arise from defects in CI assembly factors (CIAFs) that are not part of the CI holoenzyme. The biochemistry of these CIAFs is poorly defined, making their role in CI assembly unclear, and confounding interpretation of potential disease-causing genetic variants. To address these challenges, we devised a deep mutational scanning approach to systematically assess the function of thousands of NDUFAF6 genetic variants. Guided by these data, biochemical analyses and cross-linking mass spectrometry, we discovered that the CIAF NDUFAF6 facilitates incorporation of NDUFS8 into CI and reveal that NDUFS8 overexpression rectifies NDUFAF6 deficiency. Our data further provide experimental support of pathogenicity for seven novel NDUFAF6 variants associated with human pathology and introduce functional evidence for over 5,000 additional variants. Overall, our work defines the molecular function of NDUFAF6 and provides a clinical resource for aiding diagnosis of NDUFAF6-related diseases.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures




References
-
- Sazanov LA A giant molecular proton pump: structure and mechanism of respiratory complex I. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 16, 375–388 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Kirby DM et al. Respiratory chain complex I deficiency: an underdiagnosed energy generation disorder. Neurology 52, 1255–64 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Nouws J, Nijtmans LGJ, Smeitink JA & Vogel RO Assembly factors as a new class of disease genes for mitochondrial complex I deficiency: cause, pathology and treatment options. Brain 135, 12–22 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 GM131795/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35GM131795/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- T32AG000213/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000213/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- T32 GM140935/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- JP23ek0109625/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- T32 GM008505/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM140935/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- T32GM008505/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

