Boltzmann Model Predicts Glycan Structures from Lectin Binding
- PMID: 38720429
- PMCID: PMC11162346
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c04992
Boltzmann Model Predicts Glycan Structures from Lectin Binding
Abstract
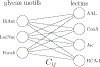
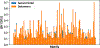
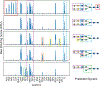
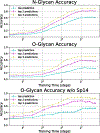
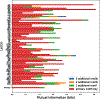
Glycans are complex oligosaccharides that are involved in many diseases and biological processes. Unfortunately, current methods for determining glycan composition and structure (glycan sequencing) are laborious and require a high level of expertise. Here, we assess the feasibility of sequencing glycans based on their lectin binding fingerprints. By training a Boltzmann model on lectin binding data, we predict the approximate structures of 88 ± 7% of N-glycans and 87 ± 13% of O-glycans in our test set. We show that our model generalizes well to the pharmaceutically relevant case of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell glycans. We also analyze the motif specificity of a wide array of lectins and identify the most and least predictive lectins and glycan features. These results could help streamline glycoprotein research and be of use to anyone using lectins for glycobiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosure
N.E.L. and A.W.T.C. have submitted patents associated with the use of lectin binding patterns for determining glycan structures and disease diagnostics. N.E.L. is also co-founder and holds financial interest in NeuImmune and Augment Biologics, which focus on glycoprotein therapeutics.
Figures


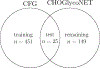

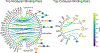
Update of
-
A Boltzmann model predicts glycan structures from lectin binding.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 12:2023.06.03.543532. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.03.543532. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Anal Chem. 2024 May 28;96(21):8332-8341. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c04992. PMID: 37333412 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hennet T Diseases of glycosylation beyond classical congenital disorders of glycosylation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 2012, 1820, 1306–1317, Glycoproteomics. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

