Improving broiler health through cecal microbiota transplantation: a comprehensive study on growth, immunity, and microbial diversity
- PMID: 38720654
- PMCID: PMC11259951
- DOI: 10.1093/jas/skae131
Improving broiler health through cecal microbiota transplantation: a comprehensive study on growth, immunity, and microbial diversity
Abstract
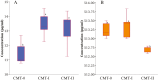
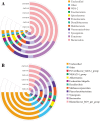
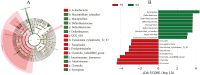
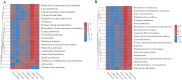
Cecal microbiota has emerged as a prominent intervention target for improving the production and welfare of poultry. This is essential for the overall health and performance of broiler chickens. The current study focused on investigating the effect of cecal microbiota transplantation (CMT) from healthy donor chickens on the growth performance, immunity, and microbial composition of newly hatched chicks and evaluated the effect of sample storage on the microbial diversity of the cecal samples. A healthy "Wannan Yellow Chicken line" was selected as the donor, and 180 1-d-old chicks from the same line were used as recipients for a 60-d feed trial. The chicks were randomly allocated to three groups (60 birds per group) with three replicates in each group. The three treatment groups were CMT-0 (control, normal saline solution), CMT-I (1:12 cecal content, normal saline supplemented with 10% glycerol), and CMT-II (1:6 cecal content, normal saline supplemented with 10% glycerol). The results of weight gain and absolute organ weight showed significant improvements in the CMT-II group compared with the CMT-0 group. Serum IgG level was significantly improved (P < 0.05) in CMT-I compared with that in the CMT-0. However, IL-6 levels increased in CMT-I and then significantly decreased in CMT-II. The cecal microbial diversity of CMT treatment was compared between two groups, fresh samples (FS) and stored samples at-80 °C (SS). The results showed that beneficial taxa, such as Firmicutes and Verrucomicrobiota, were substantially more abundant in both CMT-I and CMT-II than in CMT-0 in both FS and SS. Microbial function analysis at levels 1, 2, and 3 showed improved metabolism, genetic information processing, cellular processes, environmental information processing, and organismal systems in CMT-I and CMT-II for both FS and SS groups. However, the SS group showed decreased microbial diversity and function. To conclude, cecal microbiota transplantation is a promising strategy for enhancing the productivity and health of broiler chickens.
Keywords: cecal microbiota transplantation; chicken; growth performance; immunity; microbial diversity; storage condition.
Plain language summary
The cecal microbiota refers to a diverse community of microorganisms that play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall gut health, influencing the well-being and performance of the host bird. In this study, we aimed to improve the health and growth of broiler chickens by exploring a unique approach called cecal microbiota transplantation. A thorough investigation was conducted by transplanting the microbiota from healthy Wannan Yellow Chicken line donors into newly hatched chicks in a 60-d feeding trial. After dividing the chicks into three groups, each receiving different treatments, we found significant enhancements in WG and organ health in the groups that received cecal microbiota transplants. The results also showed improvements in Serum IgG levels in the treatment groups. Furthermore, the analysis of microbial diversity indicated that beneficial microorganisms were more abundant in the treated groups, suggesting a positive effect on chicken digestive health. To summarize, our findings suggest that transferring healthy gut microorganisms from mature parent chickens to young chicks can lead to improved growth, immune system function, microbial diversity, and overall health. This approach is a promising strategy for enhancing the productivity and well-being of broiler chickens.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society of Animal Science. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Cecal microbiota transplantation enhances calcium retention through modulation of gut microbiota and intestinal calcium transporter gene expression in chicks.Poult Sci. 2025 Sep;104(9):105437. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105437. Epub 2025 Jun 14. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40541100 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of early-life cecal microbiota transplantation from divergently selected inbred chicken lines on growth, gut serotonin, and immune parameters in recipient chickens.Poult Sci. 2022 Jul;101(7):101925. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101925. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35613492 Free PMC article.
-
Cecal Microbiota Development and Physiological Responses of Broilers Following Early Life Microbial Inoculation Using Different Delivery Methods and Microbial Sources.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 May 31;89(5):e0027123. doi: 10.1128/aem.00271-23. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37098952 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics/prebiotics effect on chicken gut microbiota and immunity in relation to heat-stress and climate-change mitigation.J Therm Biol. 2025 Apr;129:104097. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2025.104097. Epub 2025 Mar 26. J Therm Biol. 2025. PMID: 40186955 Review.
-
Heat stress and the chicken gastrointestinal microbiota: a systematic review.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 16;16(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s40104-025-01225-6. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40524217 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Eimeria challenge on growth performance, intestine integrity, and cecal microbial diversity and composition of yellow broilers.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104470. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104470. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39504824 Free PMC article.
-
Do we need a standardized 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing analysis protocol for poultry microbiota research?Poult Sci. 2025 Jul;104(7):105242. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105242. Epub 2025 May 1. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40334389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of cecal microbiota transplantation on peripheral 5-hydroxytryptamine and breast muscle glucose metabolism in long-photoperiod broilers.Poult Sci. 2025 Aug;104(8):105225. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105225. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40398302 Free PMC article.
-
Cecal microbiota transplantation enhances calcium retention through modulation of gut microbiota and intestinal calcium transporter gene expression in chicks.Poult Sci. 2025 Sep;104(9):105437. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105437. Epub 2025 Jun 14. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40541100 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the application of microbiota transplantation in chickens.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 27;16(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s40104-025-01233-6. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40571924 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Assimakopoulos, S. F., Papadopoulou I., Bantouna D., De Lastic A. -L., Rodi M., Mouzaki A., Gogos C. A., Zolota V., and Maroulis I... 2021. Fecal microbiota transplantation and hydrocortisone ameliorate intestinal barrier dysfunction and improve survival in a rat model of cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis. Shock 55:666–675. doi:10.1097/SHK.0000000000001566 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

