Knowledge mapping and research trends of exosomes in pancreatic cancer: a bibliometric analysis and review (2013-2023)
- PMID: 38720811
- PMCID: PMC11076735
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1362436
Knowledge mapping and research trends of exosomes in pancreatic cancer: a bibliometric analysis and review (2013-2023)
Abstract
Objective: This review aims to provide a quantitative and qualitative bibliometric analysis of literature from 2013 to 2023 on the role of exosomes in PC, with the goal of identifying current trends and predicting future hotspots.
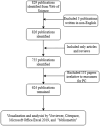
Methods: We retrieved relevant publications concerning exosomes in PC, published between 2013 and 2023, from the Web of Science Core Collection. Bibliometric analyses were conducted using VOSviewer(1.6.19), CiteSpace(6.2.R4), and Microsoft Excel (2019).
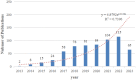
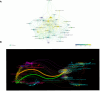
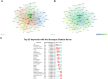
Results: A total of 624 papers were analyzed, authored by 4017 researchers from 55 countries/regions and 855 institutions, published in 258 academic journals. China (n=285, 34.42%) and the United States (n=183, 24.87%) were the most frequent contributors and collaborated closely. However, publications from China had a relatively low average number of citations (41.45 times per paper). The output of Shanghai Jiao Tong University ranked first, with 28 papers (accounting for 4.5% of the total publications). Cancers (n=31, 4.9%); published the most papers in this field. Researcher Margot Zoeller published the most papers (n=12) on this topic. Research hotspots mainly focused on the mechanisms of exosomes in PC onset and progression, the role of exosomes in PC early diagnosis and prognosis, exosomes promote the development of PC chemoresistance, and potential applications of exosomes as drug carriers for PC therapies. We observed a shift in research trends, from mechanistic studies toward clinical trials, suggesting that clinical applications will be the focus of future attention. Emerging topics were pancreatic stellate cells, diagnostic biomarkers, mesenchymal stem cells, extracellular vesicles.
Conclusion: Our scientometric and visual analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the literature on the role of exosomes in PC published during 2013-2023. This review identifies the frontiers and future directions in this area over the past decade, and is expected to provide a useful reference for researchers in this field.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOS viewer; bibliometric study; exosomes; pancreatic cancer; research hotspots.
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Feng, Wang, Zhao, Ding, Jiang, Ji, Tang and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bibliometric and visualized analysis of the applications of exosomes for bone regeneration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 17;13:1552727. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1552727. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40166633 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric and visualized analysis of extracellular vesicles in degenerative musculoskeletal diseases (from 2006 to 2024).Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 13;16:1550208. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1550208. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40183074 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge mapping of exosomes in metabolic diseases: a bibliometric analysis (2007-2022).Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 8;14:1176430. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1176430. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37223047 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements and trends in exosome research in lung cancer from a bibliometric analysis (2004-2023).Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 16;14:1358101. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1358101. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38690166 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of exosomes in sepsis from 2004 to 2022.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Aug 4;102(31):e34613. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034613. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37543762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bibliometric review of journal articles on pancreatic cancer: insights into productivity and impact.Ann Pancreat Cancer. 2025 Mar 30;8:1. doi: 10.21037/apc-24-22. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Ann Pancreat Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40727572 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome applications for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An update (Review).Oncol Rep. 2025 Jan;53(1):13. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8846. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39575479 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

