The post-septic peripheral myeloid compartment reveals unexpected diversity in myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- PMID: 38720891
- PMCID: PMC11076668
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1355405
The post-septic peripheral myeloid compartment reveals unexpected diversity in myeloid-derived suppressor cells
Abstract
Introduction: Sepsis engenders distinct host immunologic changes that include the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). These cells play a physiologic role in tempering acute inflammatory responses but can persist in patients who develop chronic critical illness.
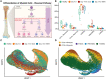
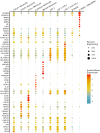
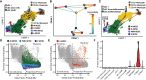
Methods: Cellular Indexing of Transcriptomes and Epitopes by Sequencing and transcriptomic analysis are used to describe MDSC subpopulations based on differential gene expression, RNA velocities, and biologic process clustering.
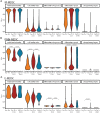
Results: We identify a unique lineage and differentiation pathway for MDSCs after sepsis and describe a novel MDSC subpopulation. Additionally, we report that the heterogeneous response of the myeloid compartment of blood to sepsis is dependent on clinical outcome.
Discussion: The origins and lineage of these MDSC subpopulations were previously assumed to be discrete and unidirectional; however, these cells exhibit a dynamic phenotype with considerable plasticity.
Keywords: chronic critical illness; myeloid-derived suppressor cells; sepsis; single-cell RNA sequencing; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2024 Barrios, Leary, Darden, Rincon, Willis, Polcz, Gillies, Munley, Dirain, Ungaro, Nacionales, Gauthier, Larson, Morel, Loftus, Mohr, Maile, Kladde, Mathews, Brusko, Brusko, Moldawer, Bacher and Efron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures





References
-
- Stortz JA, Mira JC, Raymond SL, Loftus TJ, Ozrazgat-Baslanti T, Wang Z, et al. Benchmarking clinical outcomes and the immunocatabolic phenotype of chronic critical illness after sepsis in surgical intensive care unit patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. (2018) 84:342–9. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001758 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

