Targeting CEACAM5-positive solid tumors using NILK-2401, a novel CEACAM5xCD47 κλ bispecific antibody
- PMID: 38720892
- PMCID: PMC11076849
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1378813
Targeting CEACAM5-positive solid tumors using NILK-2401, a novel CEACAM5xCD47 κλ bispecific antibody
Abstract
Background: Blocking the CD47 "don't eat me"-signal on tumor cells with monoclonal antibodies or fusion proteins has shown limited clinical activity in hematologic malignancies and solid tumors thus far. Main side effects are associated with non-tumor targeted binding to CD47 particularly on blood cells.
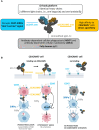
Methods: We present here the generation and preclinical development of NILK-2401, a CEACAM5×CD47 bispecific antibody (BsAb) composed of a common heavy chain and two different light chains, one kappa and one lambda, determining specificity (so-called κλ body format).
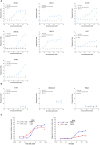
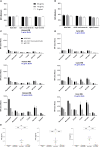
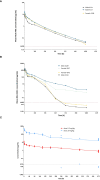
Results: NILK-2401 is a fully human BsAb binding the CEACAM5 N-terminal domain on tumor cells by its lambda light chain arm with an affinity of ≈4 nM and CD47 with its kappa chain arm with an intendedly low affinity of ≈500 nM to enabling tumor-specific blockade of the CD47-SIRPα interaction. For increased activity, NILK-2401 features a functional IgG1 Fc-part. NILK-2401 eliminates CEACAM5-positive tumor cell lines (3/3 colorectal, 2/2 gastric, 2/2 lung) with EC50 for antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity ranging from 0.38 to 25.84 nM and 0.04 to 0.25 nM, respectively. NILK-2401 binds neither CD47-positive/CEACAM5-negative cell lines nor primary epithelial cells. No erythrophagocytosis or platelet activation is observed. Quantification of the pre-existing NILK-2401-reactive T-cell repertoire in the blood of 14 healthy donors with diverse HLA molecules shows a low immunogenic potential. In vivo, NILK-2401 significantly delayed tumor growth in a NOD-SCID colon cancer model and a syngeneic mouse model using human CD47/human SIRPα transgenic mice and prolonged survival. In cynomolgus monkeys, single doses of 0.5 and 20 mg/kg were well tolerated; PK linked to anti-CD47 and Fc-binding seemed to be more than dose-proportional for Cmax and AUC0-inf. Data were validated in human FcRn TG32 mice. Combination of a CEACAM5-targeting T-cell engager (NILK-2301) with NILK-2401 can either boost NILK-2301 activity (Emax) up to 2.5-fold or allows reaching equal NILK-2301 activity at >600-fold (LS174T) to >3,000-fold (MKN-45) lower doses.
Conclusion: NILK-2401 combines promising preclinical activity with limited potential side effects due to the tumor-targeted blockade of CD47 and low immunogenicity and is planned to enter clinical testing.
Keywords: CD47; CEACAM5; bispecific antibody; immunotherapy; solid cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Seckinger, Buatois, Moine, Daubeuf, Richard, Chatel, Viandier, Bosson, Rousset, Masternak, Salgado-Pires, Batista, Mougin, Juan-Bégeot, Poitevin and Hose.
Conflict of interest statement
AS and DH declare employment at LamKap Bio Group. VB, VM, BD, FR, LC, AV, NB, ER, KM, CB, CM, FJ-B, and YP declare employment at Light Chain Bioscience - Novimmune SA. SS-P declares consultancy work for Light Chain Bioscience - Novimmune SA and LamKap Bio. The authors declare that this study received funding from LamKap Bio beta. The funder or its employees had the following involvement in the study: study design, data analysis, decision to publish, and preparation of the manuscript. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

