Comparison of upfront haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and salvage haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after immunosuppressive therapy in children with acquired severe aplastic anemia - a multicenter study
- PMID: 38720904
- PMCID: PMC11076848
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1384640
Comparison of upfront haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and salvage haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after immunosuppressive therapy in children with acquired severe aplastic anemia - a multicenter study
Abstract
Background: For children with severe aplastic anemia, if the first immunosuppressive therapy (IST) fails, it is not recommended to choose a second IST. Therefore, for patients without matched sibling donor (MSD) and matched unrelated donor (MUD), haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Haplo-HSCT) can be chosen as a salvage treatment. This article aims to explore the comparison between upfront Haplo-HSCT and salvage Haplo-HSCT after IST.
Methods: 29 patients received salvage Haplo-HSCT, and 50 patients received upfront Haplo-HSCT. The two groups received Bu (Busulfan, 3.2mg/kg/d*2d on days -9 to-8), CY (Cyclophosphamide, 60mg/kg/d*2d on days -4 to-3), Flu (fludarabine, 40mg/m2/d*5d on days -9 to -5) and rabbit ATG (Anti-thymocyte globulin, total dose 10mg/kg divided into days -4 to -2).
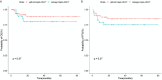
Results: The OS of the salvage Haplo-HSCT group showed no difference to the upfront Haplo-HSCT group (80.2 ± 8.0% vs. 88.7 ± 4.8%, p=0.37). The FFS of the salvage Haplo-HSCT group also showed no difference to the frontline Haplo-HSCT group (75 ± 8.2% vs. 84.9 ± 5.3%, p=0.27). There was no significant difference in the incidence of other complications after transplantation between the two groups, except for thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA). In the grouping analysis by graft source, the incidence of II-IV aGVHD in patients using PBSC ± BM+UCB was lower than that in the PBSC ± BM group (p=0.010).
Conclusion: Upfront Haplo-HSCT and salvage Haplo-HSCT after IST in children with acquired severe aplastic anemia have similar survival outcomes. However, the risk of TMA increases after salvage Haplo-HSCT. This article provides some reference value for the treatment selection of patients. In addition, co-transplantation of umbilical cord blood may reduce the incidence of GVHD.
Keywords: IST; SAA; children; multicenter study; salvage Haplo-HSCT; upfront Haplo-HSCT.
Copyright © 2024 Luo, Qu, Wang, Zhang, Sun, Xiong, Lu, Yang, Zhao, Liu and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Outcomes of Frontline Immunosuppressive Therapy and Frontline Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Children with Severe Aplastic Anemia Who Lack an HLA-Matched Sibling Donor.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019 May;25(5):975-980. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.01.017. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30658223
-
Outcomes of Matched Sibling and Haploidentical Donors Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Pediatric Severe Aplastic Anemia: A Retrospective Multicenter Study.Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2025 Apr-Jun 01;18(2):72-78. doi: 10.4103/hemoncstem.HEMONCSTEM-D-24-00037. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2025. PMID: 40538364
-
Comparison of frontline treatment with intensive immunosuppression therapy and HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for young patients with severe aplastic anemia - A meta analysis.Leuk Res. 2020 Jan;88:106266. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2019.106266. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Leuk Res. 2020. PMID: 31743865
-
The Case for Upfront HLA-Matched Unrelated Donor Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation as a Curative Option for Adult Acquired Severe Aplastic Anemia.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019 Sep;25(9):e277-e284. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.05.012. Epub 2019 May 24. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31129354 Review.
-
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in aplastic anemia: current indications and transplant strategies.Blood Rev. 2021 May;47:100772. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2020.100772. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Blood Rev. 2021. PMID: 33187812 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling new horizons in severe aplastic anemia management: a two-decade study on intensive immunosuppressive therapy combined with unrelated cord blood efficacy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 18;16:1622326. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1622326. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40755779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang XH, Chen J, Han MZ, Huang H, Jiang EL, Jiang M, et al. . The consensus from The Chinese Society of Hematology on indications, conditioning regimens and donor selection for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: 2021 update. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:145. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01159-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Bona E, Rodeghiero F, Bruno B, Gabbas A, Foa P, Locasciulli A, et al. . Rabbit antithymocyte globulin (r-ATG) plus cyclosporine and granulocyte colony stimulating factor is an effective treatment for aplastic anemia patients unresponsive to a first course of intensive immunosuppressive therapy. Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Br J Hematol. (1999) 107:330–4. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1999.01693.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical