Metabolome-wide Mendelian randomization reveals causal effects of betaine and N-acetylornithine on impairment of renal function
- PMID: 38721027
- PMCID: PMC11078220
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1371995
Metabolome-wide Mendelian randomization reveals causal effects of betaine and N-acetylornithine on impairment of renal function
Abstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common public health problem, which is characterized as impairment of renal function. The associations between blood metabolites and renal function remained unclear. This study aimed to assess the causal effect of various circulation metabolites on renal function based on metabolomics.
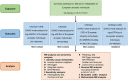
Methods: We performed a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis to estimate the causality of genetically determined metabolites on renal function. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) of 486 metabolites was used as the exposure, while summary-level data for creatinine-based estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) or CKD occurrence were set the outcomes. Inverse variance weighted (IVW) was used for primary causality analysis and other methods including weight median, MR-egger, and MR-PRESSO were applied as complementary analysis. Cochran Q test, MR-Egger intercept test, MR-PRESSO global test and leave-one-out analysis were used for sensitivity analysis. For the identified metabolites, reverse MR analysis, linkage disequilibrium score (LDSC) regression and multivariable MR (MVMR) analysis were performed for further evaluation. The causality of the identified metabolites on renal function was further validated using GWAS data for cystatin-C-based eGFR. All statistical analyses were performed in R software.
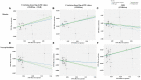
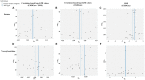
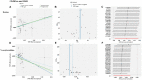
Results: In this MR analysis, a total of 44 suggestive associations corresponding to 34 known metabolites were observed. After complementary analysis and sensitivity analysis, robust causative associations between two metabolites (betaine and N-acetylornithine) and renal function were identified. Reverse MR analysis showed no causal effects of renal function on betaine and N-acetylornithine. MVMR analysis revealed that genetically predicted betaine and N-acetylornithine could directly influence independently of each other. The causal effects of betaine and N-acetylornithine were also found on cystatin-C-based eGFR.
Conclusion: Our study provided evidence to support the causal effects of betaine and N-acetylornithine on renal function. These findings required further investigations to conduct mechanism exploration and drug target selection of these identified metabolites.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; N-acetylornithine; betaine; genetically determined metabolites; renal function.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Ling, Shen and Bi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Causality of Genetically Determined Metabolites on Chronic Kidney Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study In Silico.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2024 Sep;22(7):525-550. doi: 10.1089/met.2024.0030. Epub 2024 May 14. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2024. PMID: 38742978
-
Causal effects of human serum metabolites on occurrence and progress indicators of chronic kidney disease: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Nutr. 2024 Jan 8;10:1274078. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1274078. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38260086 Free PMC article.
-
Non-targeted metabolomics revealed novel links between serum metabolites and primary ovarian insufficiency: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 26;15:1307944. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1307944. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38737546 Free PMC article.
-
The association between coffee and caffeine consumption and renal function: insight from individual-level data, Mendelian randomization, and meta-analysis.Arch Med Sci. 2021 Dec 14;18(4):900-911. doi: 10.5114/aoms/144905. eCollection 2022. Arch Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 35832703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relationship of Circulating Choline and Choline-Related Metabolite Levels with Health Outcomes: A Scoping Review of Genome-Wide Association Studies and Mendelian Randomization Studies.Adv Nutr. 2024 Feb;15(2):100164. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.100164. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Adv Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38128611 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The impact of beverage consumption on chronic renal failure risk and the mediation of serum metabolites: based on Mendelian randomization study.Genes Nutr. 2025 Jul 11;20(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12263-025-00773-w. Genes Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40646443 Free PMC article.
-
The causality between leisure sedentary behaviors, physical activity and obstructive sleep apnea: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Front Public Health. 2024 Jun 21;12:1425060. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1425060. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38975351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balint L, Socaciu C, Socaciu AI, Vlad A, Gadalean F, Bob F, et al. . Metabolites potentially derived from gut microbiota associated with podocyte, proximal tubule, and renal and cerebrovascular endothelial damage in early diabetic kidney disease in T2DM patients. Meta. (2023) 13:893. doi: 10.3390/metabo13080893, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

