Structural, functional, and dysfunctional pelvic anatomy
- PMID: 38721462
- PMCID: PMC11075961
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-23-1877
Structural, functional, and dysfunctional pelvic anatomy
Abstract
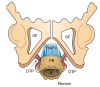
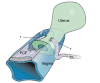
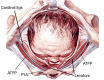
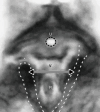
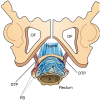
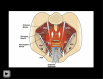
The structural basis of the Integral Theory is holistic. Four main pelvic muscles interact holistically with five main pelvic ligaments to maintain pelvic organ structure and function. The vagina is structurally weak. The support it provides to the bladder base is contingent on being stretched by opposite pelvic muscle forces, much like a trampoline. Its main role is to transmit muscle forces to facilitate continence, evacuation and control of urgency. Therefore, as an organ that cannot regenerate, the vagina should be conserved, and not excised. The ligaments provide the main structural support for the organs and are the most vulnerable part of the anatomical system to injury because their structural collagen is depolymerized prior to labour, and stretched during labour. Further ligament weakening occurs after menopause due to collagen breakdown. Hence, collagen loss is the main cause of organ prolapse and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). The strengthening of damaged ligaments, whether surgically or non-surgically, can improve or cure symptoms and prolapse. Because collagen loss in ligaments is a principal cause of dysfunction in older women, collagen-creating techniques are advised: precisely inserted tapes to create neoligaments, or wide-bore No. 2 or No. 3 polyester ligament sutures instead of dissolvable sutures.
Keywords: Pelvic organ prolapse; collagen; ligaments; lower urinary tract symptoms surgery (LUTS surgery); pelvic floor muscles.
2024 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-23-1877/coif). The series “Integral Theory Paradigm” was commissioned by the International Society for Pelviperineology without any funding or sponsorship. M.N. reports stocks and stock options at Momentis and Femselect. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures







References
-
- Petros P. The female pelvic floor function, dysfunction and management according to the Integral Theory. 3rd ed. Heidelberg: Springer Berlin; 2010.
-
- Petros PE, Swash M. The Musculo-Elastic Theory of anorectal function and dysfunction. Pelviperineology 2008;27:89-121.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
