Artificial intelligence for the detection of glaucoma with SD-OCT images: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 38721504
- PMCID: PMC11074164
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2024.03.02
Artificial intelligence for the detection of glaucoma with SD-OCT images: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To quantify the performance of artificial intelligence (AI) in detecting glaucoma with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) images.
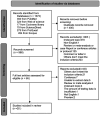
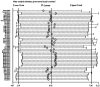
Methods: Electronic databases including PubMed, Embase, Scopus, ScienceDirect, ProQuest and Cochrane Library were searched before May 31, 2023 which adopted AI for glaucoma detection with SD-OCT images. All pieces of the literature were screened and extracted by two investigators. Meta-analysis, Meta-regression, subgroup, and publication of bias were conducted by Stata16.0. The risk of bias assessment was performed in Revman5.4 using the QUADAS-2 tool.
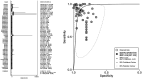
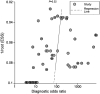
Results: Twenty studies and 51 models were selected for systematic review and Meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.91 (95%CI: 0.86-0.94, I2=94.67%), 0.90 (95%CI: 0.87-0.92, I2=89.24%). The pooled positive likelihood ratio (PLR) and negative likelihood ratio (NLR) were 8.79 (95%CI: 6.93-11.15, I2=89.31%) and 0.11 (95%CI: 0.07-0.16, I2=95.25%). The pooled diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) and area under curve (AUC) were 83.58 (95%CI: 47.15-148.15, I2=100%) and 0.95 (95%CI: 0.93-0.97). There was no threshold effect (Spearman correlation coefficient=0.22, P>0.05).
Conclusion: There is a high accuracy for the detection of glaucoma with AI with SD-OCT images. The application of AI-based algorithms allows together with "doctor+artificial intelligence" to improve the diagnosis of glaucoma.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; artificial intelligence; glaucoma; spectral-domain optical coherence tomography.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Shi NN, None; Li J, None; Liu GH, None; Cao MF, None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Compared to Biopsy in Detecting Early Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Aug 1;25(8):2593-2603. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.8.2593. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39205556 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Glaucoma Screening and Clinical Practice.J Glaucoma. 2022 May 1;31(5):285-299. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000002015. Epub 2022 Mar 18. J Glaucoma. 2022. PMID: 35302538
-
Accuracy of artificial intelligence in detecting tumor bone metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 18;25(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13631-0. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39966724 Free PMC article.
-
Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of subepithelial lesions using endoscopic ultrasonography: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 15;12:915481. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.915481. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36046054 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Endoscopic Diagnosis of Early Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 10;12:855175. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.855175. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35756602 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Deep Learning in Glaucoma Detection and Progression Prediction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 10;13(2):420. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020420. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning for the prediction of diabetes-related amputation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy.Clin Exp Med. 2025 May 10;25(1):151. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01697-w. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40348887 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T, Cheng CY. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(11):2081–2090. - PubMed
-
- Weinreb RN, Khaw PT. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet. 2004;363(9422):1711–1720. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
