Robotic versus laparoscopic versus open nephrectomy for live kidney donors
- PMID: 38721875
- PMCID: PMC11079970
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006124.pub3
Robotic versus laparoscopic versus open nephrectomy for live kidney donors
Abstract
Background: Waiting lists for kidney transplantation continue to grow. Live kidney donation significantly reduces waiting times and improves long-term outcomes for recipients. Major disincentives to potential kidney donors are the pain and morbidity associated with surgery. This is an update of a review published in 2011.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and harms of open donor nephrectomy (ODN), laparoscopic donor nephrectomy (LDN), hand-assisted LDN (HALDN) and robotic donor nephrectomy (RDN) as appropriate surgical techniques for live kidney donors.
Search methods: We contacted the Information Specialist and searched the Cochrane Kidney and Transplant Register of Studies up to 31 March 2024 using search terms relevant to this review. Studies in the Register are identified through searches of CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and EMBASE, conference proceedings, the International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) Search Portal, and ClinicalTrials.gov.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing LDN with ODN, HALDN, or RDN were included.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently screened titles and abstracts for eligibility, assessed study quality, and extracted data. We contacted study authors for additional information where necessary. Summary estimates of effect were obtained using a random-effects model, and results were expressed as risk ratios (RR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) for dichotomous outcomes and mean difference (MD) or standardised mean difference (SMD) and 95% CI for continuous outcomes. Confidence in the evidence was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach.
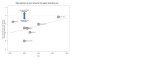
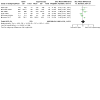
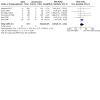
Main results: Thirteen studies randomising 1280 live kidney donors to ODN, LDN, HALDN, or RDN were included. All studies were assessed as having a low or unclear risk of bias for selection bias. Five studies had a high risk of bias for blinding. Seven studies randomised 815 live kidney donors to LDN or ODN. LDN was associated with reduced analgesia use (high certainty evidence) and shorter hospital stay, a longer procedure and longer warm ischaemia time (moderate certainty evidence). There were no overall differences in blood loss, perioperative complications, or need for operations (low or very low certainty evidence). Three studies randomised 270 live kidney donors to LDN or HALDN. There were no differences between HALDN and LDN for analgesia requirement, hospital stay (high certainty evidence), duration of procedure (moderate certainty evidence), blood loss, perioperative complications, or reoperations (low certainty evidence). The evidence for warm ischaemia time was very uncertain due to high heterogeneity. One study randomised 50 live kidney donors to retroperitoneal ODN or HALDN and reported less pain and analgesia requirements with ODN. It found decreased blood loss and duration of the procedure with HALDN. No differences were found in perioperative complications, reoperations, hospital stay, or primary warm ischaemia time. One study randomised 45 live kidney donors to LDN or RDN and reported a longer warm ischaemia time with RDN but no differences in analgesia requirement, duration of procedure, blood loss, perioperative complications, reoperations, or hospital stay. One study randomised 100 live kidney donors to two variations of LDN and reported no differences in hospital stay, duration of procedure, conversion rates, primary warm ischaemia times, or complications (not meta-analysed). The conversion rates to ODN were 6/587 (1.02%) in LDN, 1/160 (0.63%) in HALDN, and 0/15 in RDN. Graft outcomes were rarely or selectively reported across the studies. There were no differences between LDN and ODN for early graft loss, delayed graft function, acute rejection, ureteric complications, kidney function or one-year graft loss. In a meta-regression analysis between LDN and ODN, moderate certainty evidence on procedure duration changed significantly in favour of LDN over time (yearly reduction = 7.12 min, 95% CI 2.56 to 11.67; P = 0.0022). Differences in very low certainty evidence on perioperative complications also changed significantly in favour of LDN over time (yearly change in LnRR = 0.107, 95% CI 0.022 to 0.192; P = 0.014). Various different combinations of techniques were used in each study, resulting in heterogeneity among the results.
Authors' conclusions: LDN is associated with less pain compared to ODN and has comparable pain to HALDN and RDN. HALDN is comparable to LDN in all outcomes except warm ischaemia time, which may be associated with a reduction. One study reported kidneys obtained during RDN had greater warm ischaemia times. Complications and occurrences of perioperative events needing further intervention were equivalent between all methods.
Copyright © 2024 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Georgios Kourounis: No relevant interests were disclosed
Sam Tingle: No relevant interests were disclosed
Thomas Hoather: No relevant interests were disclosed
Emma Thompson: No relevant interests were disclosed
Alistair Rogers: No relevant interests were disclosed
Tobias Page: No relevant interests were disclosed
Aliu Sanni: No relevant interests were disclosed
David Rix: No relevant interests were disclosed
Naeem Soomro: No relevant interests were disclosed
Colin Wilson: No relevant interests were disclosed
Figures
























Update of
-
Laparoscopic versus open nephrectomy for live kidney donors.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Nov 9;(11):CD006124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006124.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 9;5:CD006124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006124.pub3. PMID: 22071829 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Bargman 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bargman V, Sundaram CP, Bernie J, Goggins W. Randomized trial of laparoscopic donor nephrectomy with and without hand assistance. Journal of Endourology 2006;20(10):717-22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Basiri 2007 {published data only}
-
- Basiri A, Simforoosh N, Heidari M, Moghaddam SM, Otookesh H. Laparoscopic v open donor nephrectomy for pediatric kidney recipients: preliminary report of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Endourology 2007;21(9):1033-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bhattu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Bhattu AS, Ganpule A, Sabnis RB, Murali V, Mishra S, Desai M. Robot-assisted laparoscopic donor nephrectomy vs standard laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: a prospective randomized comparative study. Journal of Endourology 2015;29(12):1334-40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
HARP 2010 {published data only}
-
- Dols LF, Kok NF, Khe Tran TC, Terkivatan T, D'Ancona FC, Langenhuijsen JF, et al. Hand-assisted retroperitoneoscopic versus standard laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: single blind, randomised controlled trial [abstract no: O-088]. Transplant International 2011;24(Suppl 2):25. [EMBASE: 70527166]
-
- Dols LF, Kok NF, Tran TC, Terkivatan T, D'Ancona FC, Langenhuijsen JF, et al. Hand-assisted retroperitoneoscopic versus standard laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: single blind, randomised controlled trial [abstract no: 345]. American Journal of Transplantation 2011;11:134-5. [EMBASE: 70405379]
-
- Dols LF, Kok NF, d'Ancona FC, Klop KW, Tran TC, Langenhuijsen JF, et al. Randomized controlled trial comparing hand-assisted retroperitoneoscopic versus standard laparoscopic donor nephrectomy. Transplantation 2014;97(2):161-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Janki S, Dols LF, Mulder EE, Tran KT, Betjes MG, Dooper IM, et al. A 5-year analysis after live donor nephrectomy within the era of extended criteria donors-identifying factors for decline of kidney function [abstract no: 422.9]. Transplantation 2016;100(7 Suppl 1):S183. [EMBASE: 613005179]
HARP II 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Klop KW, Kok NF, Dols LF, Dor FJ, Tran KT, Terkivatan T, et al. Can right-sided hand-assisted retroperitoneoscopic donor nephrectomy be advocated above standard laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: a randomized pilot study. Transplant International 2014;27(2):162-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hofker 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hofker HS, Nijboer WN, Krikke C, Niesing J, Heide JJH, De Maar E, et al. A prospective randomized study comparing minimal invasive open and laparoscopic (HAL) living donor nephrectomy [abstract]. Transplant International 2007;20(Suppl 2):184. [CENTRAL: CN-0074054]
-
- Hofker HS, Nijboer WN, Niesing J, Krikke C, Seelen MA, Son WJ, et al. A randomized clinical trial of living donor nephrectomy: a plea for a differentiated appraisal of mini-open muscle splitting incision and hand-assisted laparoscopic donor nephrectomy. Transplant International 2012;25(9):976-86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kok 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Dols LF, Ijzermans JN, Wentink N, Tran TC, Zuidema WC, Dooper IM, et al. Long-term follow-up of a randomized trial comparing laparoscopic and mini-incision open live donor nephrectomy. American Journal of Transplantation 2010;10(11):2481-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Dols LF, Kok NF, Wentink N, Tran KT, Zuidema WC, Dooper IM, et al. Long-term follow-up of a randomized trial comparing laparoscopic and mini-incision open donor nephrectomy [abstract no: P836]. Transplant International 2009;22(Suppl 2):302. - PubMed
-
- Janki S, Klop K, Dooper I, Weimar W, Ijzermans J, Kok N. Ten-year follow-up after live kidney donation - a prospective cohort study [abstract no: P018]. In: British Transplantation Society & Nederlandse Transplantatie Vereniging Joint Congress; 2015 Mar 11-13; Bournemouth, UK. 2015.
-
- Janki S, Klop K, Dooper I, Weimar W, Ijzermans J, Kok N. Ten-year follow-up after live kidney donation-a prospective cohort study [abstract no: B191]. American Journal of Transplantation 2015;15(Suppl 3). [EMBASE: 71954421]
-
- Kok NF, Adang EM, Hansson BM, Dooper IM, Weimar W, Wilt GJ, et al. Cost effectiveness of laparoscopic versus mini-incision open donor nephrectomy: a randomized study. Transplantation 2007;83(12):1582-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mansour 2017 {published data only}
-
- Mansour AM, El-Nahas AR, Ali-El-Dein B, Denewar AA, Abbas MA, Abdel-Rahman A, et al. Enhanced recovery open vs laparoscopic left donor nephrectomy: a randomized controlled trial. Urology 2017;110:98-103. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nicholson 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Brook NR, Harper SJ, Bagul A, Elwell R, Nicholson ML. Laparoscopic donor nephrectomy yields kidneys with structure and function equivalent to those retrieved by open surgery. Transplantation Proceedings 2005;37(2):625-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Brook NR, Lewis GR, Waller JR, Bains JC, Harper S, Elwell R, et al. Laparoscopic donor nephrectomy yields kidneys that are structurally and functionally equivalent to those procured by open surgery - results of a randomised trial [abstract no: P148]. Transplantation 2004;78(2 Suppl):244. [CENTRAL: CN-01657241]
-
- Brook NR, Lewis GR, Waller JR, Bains JC, Veitch PS, Nicholson ML. Laparoscopic donor nephrectomy yields kidneys that are structurally and functionally equivalent to those procured by open surgery - results of a randomised trial [abstract no: 1205]. American Journal of Transplantation 2004;4(Suppl 8):488. [CENTRAL: CN-00509105]
-
- Elwell R, Bagul A, Moorhouse J, Veitch PS, Nicholson ML. Medium-term follow up of renal transplant recipients from a randomised controlled trial of laparoscopic versus open live donor nephrectomy [abstract no: O-226]. Transplant International 2009;22(Suppl 2):59-60.
-
- Kaushik M, Elwell R, Bagul A, Veitch P, Nicholson M. Medium-term follow up of renal transplant recipients from a randomised controlled trial of laparoscopic versus open live donor nephrectomy [abstract no: O59]. In: British Transplantation Society (BTS).12th Annual Congress; 2009 Apr 21-24; Liverpool, UK. 2009. [CENTRAL: CN-01658565]
Oyen 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Andersen MH, Mathisen L, Oyen O, Edwin B, Digernes R, Kvarstein G, et al. Postoperative pain and convalescence in living kidney donors-laparoscopic versus open donor nephrectomy: a randomized study. American Journal of Transplantation 2006;6(6):1438-43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Andersen MH, Mathisen L, Veenstra M, Oyen O, Edwin B, Digernes R, et al. Quality of life after randomization to laparoscopic versus open living donor nephrectomy: long-term follow-up. Transplantation 2007;84(1):64-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hamidi V, Andersen MH, Oyen O, Mathisen L, Fosse E, Kristiansen IS. Cost effectiveness of open versus laparoscopic living-donor nephrectomy. Transplantation 2009;87(6):831-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Oyen O, Andersen M, Mathisen L, Kvarstein G, Edwin B, Line PD, et al. Laparoscopic versus open living-donor nephrectomy: experiences from a prospective, randomized, single-center study focusing on donor safety. Transplantation 2005;79(9):1236-40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Oyen O, Line PD, Pfeffer P, Edwin B, Jorgensen PF, Foss A, et al. Laparoscopic living donor nephrectomy: introduction of simple hand-assisted technique (without handport). Transplantation Proceedings 2003;35(2):779-81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simforoosh 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Simforoosh N, Basiri A, Shakhssalim N, Gooran S, Tabibi A, Khoshdel A, et al. Long-term graft function in a randomized clinical trial comparing laparoscopic versus open donor nephrectomy. Experimental & Clinical Transplantation 2012;10(5):428-32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Simforoosh N, Basiri A, Tabibi A, Shakhssalim N, Hosseini Moghaddam SM. Comparison of laparoscopic and open donor nephrectomy: a randomized controlled trial. BJU International 2005;95(6):851-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Simforoosh N, Basiri A, Ziaei SAM, Tabibi A, Salim NS, Pourrezagholi F, et al. Laparoscopic versus open live donor nephrectomy. The first prospective clinical trial [abstract no: 1319]. American Journal of Transplantation 2003;3(Suppl 5):490. [CENTRAL: CN-00447743] - PubMed
-
- Simforoosh N, Bassiri A, Ziaee SA, Tabibi A, Salim NS, Pourrezagholi F, et al. Laparoscopic versus open live donor nephrectomy: the first randomized clinical trial. Transplantation Proceedings 2003;35(7):2553-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Simforoosh NI, Basiri A, Shakhssalim N, Gooran S, Tabibi A, Khoshdel A, et al. Long term graft function in a randomized clinical trial comparing laparoscopic versus open donor nephrectomy [abstract]. Journal of Endourology 2011;25(Suppl 1):A76-7. [EMBASE: 70584875] - PubMed
Simforoosh 2015 {published data only}
-
- Simforoosh N, Hosseini Sharifi SH, Valipour R, Narouie B, Kamranmanesh MR, Soltani MH. Minilaparoscopy vs. standard laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: comparison of safety, efficacy and cosmetic outcomes in a randomized clinical trial. Urology Journal 2015;12(4):2223-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wolf 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wolf JS Jr, Merion RM, Leichtman AB, Campbell DA, Magee JC, Punch JD, et al. Randomized controlled trial of hand-assisted laparoscopic versus open surgical live donor nephrectomy. Transplantation 2001;72(2):284-90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Donaldson 2004 {published data only}N0254147344
-
- Donaldson P. Prospective randomised trial of laparoscopic versus open nephrectomy. National Research Register, UK [http://www.nrr.nhs.uk/] (last accessed 2004).
Guleria 2010 {published data only}
-
- Guleria S, Kumar R, Reddy S, Jain S, Aggarwall S, Mahajan S, et al. Is laparoscopic donor nephrectomy really the way ahead? [abstract no: 355]. Transplantation 2008;86(2S):125.
Seneviratne 2018 {published data only}
-
- Seneviratne L, Hingalagoda C, Mannikage Y, Udurawana S, Pilimatalawwe C. Total laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy: Comparison study between robotic arm assisted 3D laparoscopy and standard 2D laparoscopic donor nephrectomy [abstract][VL - 102. Transplantation 2018;7(Suppl 1):S338. [EMBASE: 623702341]
References to ongoing studies
ChiCTR‐TRC‐10000870 {published data only}
-
- Qiang Z. A prospective randomized controlled trial of open or modified laparoscopic techniques in living donor nephrectomy. www.chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=8667 (first received 19 April 2010).
Additional references
Akin 2021
-
- Akin E, Altintoprak F, Firat N, Dheir H, Bas E, Demirci T, et al. Is laparoscopic technique suitable for initial experience in live donor nephrectomy? Results of the first 51 cases. Electronic Journal of General Medicine 2021;18(6):em326. [EMBASE: 2014462221]
Bailey 2016
-
- Bailey P, Edwards A, Courtney AE. Living kidney donation. BMJ 2016;354:i4746. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Broe 2018
Brook 2005
-
- Brook NR, Wilson CH, Nicholson ML. Current status of live donor renal transplantation. Therapy 2005;2(6):909-20. [EMBASE: 2005544719]
BTS/RA Guidelines 2018
-
- British Transplantation Society and Renal Association. Chapter 6. Surgery: technical aspects, donor risk and peri-operative care. In: Living Donor Kidney Transplantation Guidelines 2018. Fourth edition. London: BTS, 2018:171-90.
Cecka 1995
-
- Cecka JM. Living donor transplants. In: Cecka JM, Terasaki Pl, editors(s). Clinical Transplants. Los Angeles: UCLA Tissue Typing Laboratory, 1995:263-77.
Dols 2009
-
- Dols LF, Kok NF, Ijzermans JN. Live donor nephrectomy: a review of evidence for surgical techniques. Transplant International 2010;23(2):121-30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Egger 1997
Fabrizio 1999
-
- Fabrizio MD, Ratner LE, Montgomery RA, Kavoussi LR. Laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy. Urologic Clinics of North America 1999;26(1):247-56. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Giessieng 2004
-
- Giessieng M. Laparoscopic living donor nephrectomy. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2004;19 Suppl 4:iv36-40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
GRADE 2008
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2022
-
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Jacobs 2004
-
- Jacobs SC, Cho E, Foster C, Liao P, Bartlett ST. Laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: The University of Maryland 6-Year experience. Journal of Urology 2004;171(1):47-51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
KDIGO Guidelines 2017
Mjoen 2009
-
- Mjoen G, Oyen O, Holdaas H, Midtvedt K, Line PD. Morbidity and mortality in 1022 consecutive living donor nephrectomies: benefits of a living donor registry. Transplantation 2009;88(11):1273-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NHSBT Living Donor Kidney Transplant
-
- NHSBT Living donor kidney transplant. https://www.nhsbt.nhs.uk/organ-transplantation/kidney/receiving-a-kidney... (accessed 31 March 2024).
Peters 2002
-
- Peters TG, Repper SM, Vincent MC, Schonberg CA, Jones KW, Cruz I, et al. One hundred consecutive living kidney donors: modern issues and outcomes. Clinical Transplantation 2002;16 Suppl 7:62-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rally 2020
-
- Rally S, Sharma A, Singh S, Patil SS, Pandey GS, Kapoor K, et al. Experience with 15 years of laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: review of 2500 cases.. Transplantation Proceedings 2020;52(6):1671-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ratner 1995
-
- Ratner LE, Ciseck LJ, Moore RG, Cigarroa FG, Kaufman HS, Kavoussi LR. Laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy. Transplantation 1995;60(9):1047-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ratner 1997
-
- Ratner LE, Hiller J, Sroka M, Weber R, Sikorsky I, Montgomery RA, et al. Laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy removes disincentives to live donation. Transplantation Proceedings 1997;29(8):3402-3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Salazar 2005
-
- Salazar A, Pelletier R, Yilmaz S, Monroy-Cuadros M, Tibbles LA, McLaughlin K, et al. Use of a minimally invasive donor nephrectomy program to select technique for live donor nephrectomy. American Journal of Surgery 2005;189(5):558-62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Siddique 2020
Takagi 2021
-
- Takagi K, Kimenai HJ, Terkivatan T, Tran KT, Ijzermans JN, Minnee RC. Learning curves of minimally invasive donor nephrectomy in a high-volume center: A cohort study of 1895 consecutive living donors. International Journal of Surgery 2021;86:7-12. [PMID: ] - PubMed
UNOS 1996
-
- UNOS, Division of Transplantation, Bureau of Health Resources Development. Annual report of the US scientific registry of transplant recipients and the organ procurement and transplantation network - transplant data: 1988-95. Richmond: US Department of Health and Human Services, 1996.
van der Merwe 2021
-
- Merwe A, Ebinger Mundorf, NN, Heerden H, Bonkat G, Deventer H, Mantica G, et al. Evaluating the differences in the early laparoscopic donor nephrectomy learning curves of a Swiss high volume transplant program and a South African low volume transplant program after knowledge transfer. African Journal of Urology 2021;27(1):119. [EMBASE: 2013497124]
Wolfe 1999
-
- Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL, Ojo AO, Ettenger RE, Agodoa LY, et al. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. New England Journal of Medicine 1999;341(23):1725-30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Sanni 2006
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

