Geriatric nutritional risk index is associated with the occurrence of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with acute heart failure
- PMID: 38721891
- PMCID: PMC11085996
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2349122
Geriatric nutritional risk index is associated with the occurrence of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with acute heart failure
Abstract
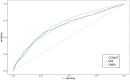
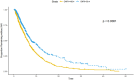
Background: During the acute heart failure (AHF), acute kidney injury (AKI) is highly prevalent in critically ill patients. The occurrence of the latter condition increases the risk of mortality in patients with acute heart failure. The current research on the relationship between nutritional risk and the occurrence of acute kidney injury in patients with acute heart failure is very limited. Methods: This retrospective cohort study utilized data from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV (MIMIC-IV, version 2.1) database. We included adult patients with AHF who were admitted to the intensive care unit in the study. Results: A total of 1310 critically ill patients with acute heart failure were included. The AUC of geriatric nutritional risk index (GNRI) (0.694) is slightly superior to that of controlling nutritional status (CONUT) (0.656) and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) (0.669). The Log-rank test revealed a higher risk of acute kidney injury in patients with high nutritional risk (p < 0.001). Multivariate COX regression analysis indicated that a high GNRI (adjusted HR 0.62, p < 0.001) was associated with a reduced risk of AKI during hospitalization in AHF patients. The final subgroup analysis demonstrated no significant interaction of GNRI in all subgroups except for diabetes subgroup and ventilation subgroup (P for interaction: 0.057-0.785). Conclusion: Our study findings suggest a correlation between GNRI and the occurrence of acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with acute heart failure.
Keywords: Acute heart failure; acute kidney injury; malnutrition; nutrition assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index on short-term prognosis of patients with sepsis-related acute kidney injury: analysis using the MIMIC-IV database.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Apr 23;26(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04122-2. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40269775 Free PMC article.
-
Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index and Risk of Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Acute Kidney Injury: A Multicenter Cohort Study.J Ren Nutr. 2023 Sep;33(5):639-648. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2023.06.004. Epub 2023 Jun 10. J Ren Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37302721
-
The relationship between Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index (GNRI) and in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI).BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Sep 6;24(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02689-1. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39242503 Free PMC article.
-
Geriatric nutritional risk index predicts all-cause mortality in patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021 Mar 24;76:e2258. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2258. eCollection 2021. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021. PMID: 33787674 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of geriatric nutritional risk index in elderly patients with heart failure: a meta-analysis.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021 Jun;33(6):1477-1486. doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01656-3. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 32766928 Review.
Cited by
-
Malnutrition Evaluated by CONUT Score and Its Association With Acute Kidney Injury in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients: A Retrospective Study.Cardiol Res Pract. 2025 Jul 10;2025:1118619. doi: 10.1155/crp/1118619. eCollection 2025. Cardiol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 40688635 Free PMC article.
-
The association between Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index and KSD disease: results from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2018.Front Nutr. 2024 Nov 6;11:1430668. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1430668. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39574520 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index on short-term prognosis of patients with sepsis-related acute kidney injury: analysis using the MIMIC-IV database.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Apr 23;26(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04122-2. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40269775 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
