Protocol to develop human alveolar macrophage-like cells from mononuclear cells or purified monocytes for use in respiratory biology research
- PMID: 38722740
- PMCID: PMC11099312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2024.103061
Protocol to develop human alveolar macrophage-like cells from mononuclear cells or purified monocytes for use in respiratory biology research
Abstract
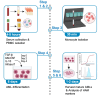
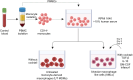
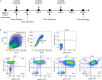
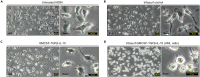
Human alveolar macrophages are a unique myeloid subset critical for understanding pulmonary diseases and are difficult to access. Here, we present a protocol to generate human alveolar macrophage-like (AML) cells from fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells or purified monocytes. We describe steps for cell isolation, incubation in a defined cocktail of pulmonary surfactant and lung-associated cytokines, phenotype analysis, and validation with human alveolar macrophages. We then detail procedures for quality control and technical readouts for monitoring microbial response. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Pahari et al.1 and Neehus et al.2.
Keywords: cell biology; cell culture; cell isolation; flow cytometry; immunology.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A non-provisional patent application has been filed with the number 17/657,344 for an invention titled “Cell culture media and methods for generating human Alveolar Macrophage-Like cells.” The applicant is the Texas Biomedical Research Institute, located in San Antonio, Texas, USA. The inventors listed in the application are L.S.S. and S.P., both from San Antonio, Texas, USA. For more details, please refer to the following link: https://patentcenter.uspto.gov/applications/17657344.
Figures


References
-
- Pahari S., Arnett E., Simper J., Azad A., Guerrero-Arguero I., Ye C., Zhang H., Cai H., Wang Y., Lai Z., et al. A new tractable method for generating human alveolar macrophage-like cells in vitro to study lung inflammatory processes and diseases. mBio. 2023;14 doi: 10.1128/mbio.00834-23. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neehus A.L., Carey B., Landekic M., Panikulam P., Deutsch G., Ogishi M., Arango-Franco C.A., Philippot Q., Modaresi M., Mohammadzadeh I., et al. Human inherited CCR2 deficiency underlies progressive polycystic lung disease. Cell. 2024;187:390–408.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.11.036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Papp A.C., Azad A.K., Pietrzak M., Williams A., Handelman S.K., Igo R.P., Jr., Stein C.M., Hartmann K., Schlesinger L.S., Sadee W. AmpliSeq transcriptome analysis of human alveolar and monocyte-derived macrophages over time in response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. PLoS One. 2018;13 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198221. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

